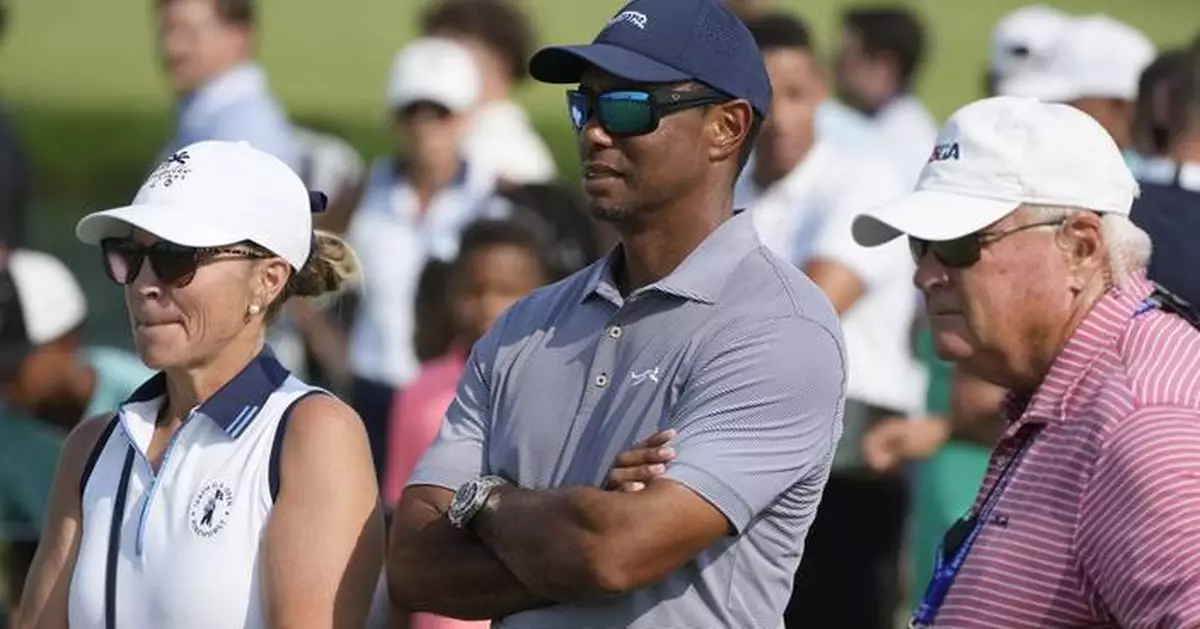
Tiger Woods could not offer much of a timetable Tuesday on PGA Tour negotiations with the Saudi backers of LIV Golf or his own future as a player.
Woods is the tournament host of the Hero World Challenge this week, and that's his only role at Albany Golf Club in the Bahamas. He has played the holiday tournament only once since 2019, missing this year while recovering from a sixth surgery on his lower back.
“I'm not tournament sharp yet, no. I'm still not there,” Woods said. “These are 20 of the best players in the world and I'm not sharp enough to compete against them at this level. So when I'm ready to compete and play at this level, then I will.”
A big part of his time is occupied by PGA Tour business matters. Woods was appointed to the PGA Tour board a year ago with no term limits, and he also is on the board of the commercial PGA Tour Enterprises.
There has been movement on negotiations for the Public Investment Fund of Saudi Arabia to become a minority investor in PGA Tour Enterprises — the tour already has a $1.5 billion investment from Strategic Sports Group and a player equity program. PGA Tour Commissioner Jay Monahan played in the Dunhill Links Championship on the European tour with the PIF governor, Yasir Al-Rumayyan.
Monahan also played golf with President-elect Donald Trump, who had said he could fix golf's mess in about 15 minutes.
“I think all of us who have been a part of this process would have thought it would have happened quicker than this,” Woods said.
He suggested any deal still would have required Justice Department approval.
“But things are very fluid, we’re still working through it, it’s happening daily,” Woods said. “From a policy board standpoint or from an enterprise standpoint, things are moving and they’re constructive.”
In the meantime, Bloomberg reported last week the European tour is talking with PIF separately, leading to suggestions of a shared schedule in which players from the European tour and LIV Golf could play on each circuit.
“We all want to get past this and to do what’s best for the tour and in trying to do that, there’s going to be ... some eggs are going to be knocked over and it’s going to be a little bit difficult at times,” Woods said. “But in the end we’re going to get a product that’s better for all the fans and all the players that are involved and get some peace that the game desperately needs.”
As for his own future, Woods was not certain. He was not asked if he planned to play in two weeks at the PNC Championship with his son, Charlie. It's a 36-hole event hosted by the PGA Tour Champions, so Woods could ride in a cart. He has played it each of the last four years.
He looked back at 2024 as a lost year, primarily because of his ailing back that began to spasm as the year went on.
Woods had set a goal of playing a big tournament once a month through the majors season, but that fell apart early when he missed The Players Championship in March. He set a Masters record by making his 24th consecutive cut, but then only played at the next three majors and was gone by the weekend at each of them.
He had a microdiscectomy in September to alleviate pain down his legs, but he had no idea how often he could play in 2025.
“Whether my commitment going forward is once a month, yeah, I could say that all over again,” Woods said. "But I truly don’t know. I’m just trying to rehab and still get stronger and better and feel better, really give myself the best chance I can going into next year.
“This year, I had to toss it away and I wasn’t as sharp as I needed to be and I didn’t play as much as I needed to going into the major championships and I didn’t play well at them,” he said. “Hopefully next year will be better. I’ll be physically stronger and better. I know the procedure helped and hopefully that I can then build upon that.”
AP golf: https://apnews.com/hub/golf
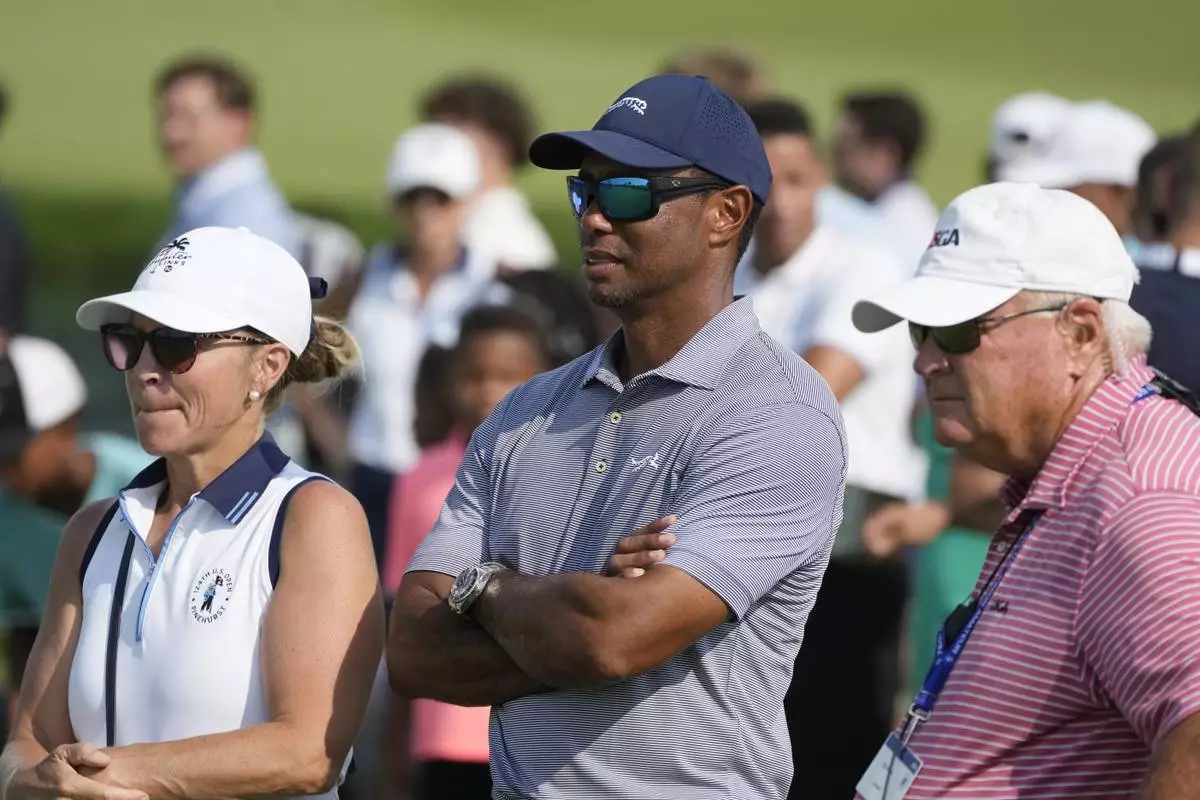

FILE - Tiger Woods watches his son Charlie Woods during the second round of stroke play at the U.S. Junior Amateur Golf Championship on July 23, 2024, in Bloomfield Township, Mich. (AP Photo/Carlos Osorio, File)