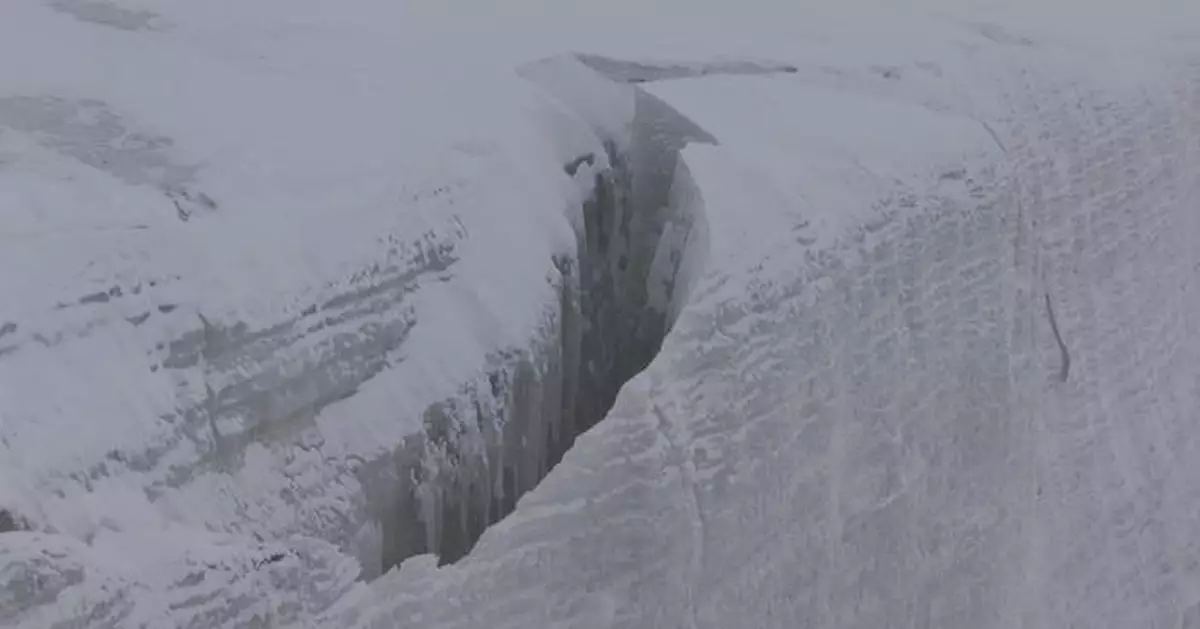
The third Chinese Glacier Inventory was released by the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources on Friday at a time of the first ever World Day for Glaciers.
The inventory shows that as of around 2020, China's total glacier area was approximately 46,000 square kilometers with roughly 69,000 individual glaciers.
Compared with data from the second Chinese Glacier Inventory published in 2014, the total glacier area in the period of 2008 to 2020 dropped around 6 percent.
When compared to data from the first Chinese Glacier Inventory published in 2002, China's total glacier area in the period of 1960 to 2020 decreased by approximately 26 percent.
Among regions experiencing severe declines, glaciers in the Nianqing Tanggula Mountains and the Altai Mountains have retreated by over 45 percent, while those in the Hengduan Mountains and the Himalayas Mountain range have shrunk by more than 35 percent. The Qilian Mountains and the Tianshan Mountains have lost approximately 30 percent of their glacier area.
The Kunlun Mountains and the Karakoram Mountains have experienced the least reduction, with retreat rates of 1 percent and 7 percent, respectively.
The United Nations General Assembly designated March 21 as World Day for Glaciers in a resolution adopted in December 2022, and also, declared 2025 as the International Year of Glaciers' Preservation, to raise global awareness about the critical role of glaciers in the climate system, and to address the impacts of the impending changes in the planet's cryosphere.
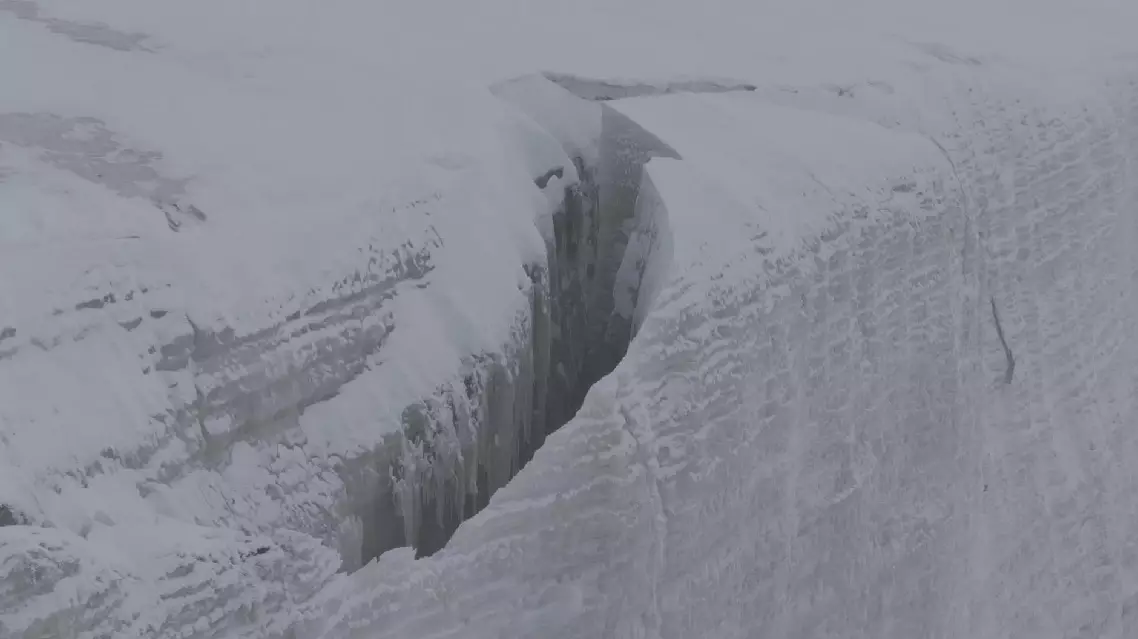

China releases third Chinese Glacier Inventory