The suburban reservoirs that supply 10% of New York City's vaunted drinking water are getting saltier due to decades of road salt being spread near the system — and they will eventually have to be abandoned if nothing is done to reverse the trend, city officials warn.
The plug wouldn't have to be pulled until early next century, according to a new study. But the soaring saltiness could eventually affect the famous taste of the Big Apple’s water, which is sometimes called the champagne of tap water, and poses a challenge to managers of a system that serves more than 9 million people.
“The conclusion of this study is that if we don’t change our ways, in 2100 the Croton Water System becomes a nice recreational facility, but it ceases to be a water supply,” Rohit Aggarwala, the city’s environmental protection commissioner, said in an interview with The Associated Press. “And that will directly impact everybody who drinks New York City water.”
The Croton system dates back to 1842 — when the first Croton Aqueduct began delivering water to a reservoir in what is now Manhattan’s Central Park — and is now comprised of 12 reservoirs and three controlled lakes north of the city.
The report found the concentration of chlorides — an indicator of salinization — tripled from 1987 to 2019 in the system's main reservoir, which is about 20 miles (32 kilometers) north of the city line. Concentrations are on track to exceed the state’s maximum contaminant level for chloride by 2108.
The report found salinity increases across the sprawling system of city reservoirs in upstate New York. However, the problem is far less of an issue in the Delaware and Catskill watersheds west of the Hudson River, which supply about 90% of the city’s water. That’s likely because there’s far less development in those watersheds.
Road salt is considered a main driver of the increase, along with sewage treatment plant discharges and water softeners. Millions of tons of rock salt is spread on U.S. roads each winter as a cheap and effective way to reduce accidents.
“It's really a problem across the country in areas with a lot of snow,” said Shannon Roback, science director for the environmental group Riverkeeper. “We’ve seen rising levels of salt in water in the Northeast, in the Midwest and in most places that use road salt.”
Roback noted that high salt levels in drinking water pose a host of environmental concerns and can be harmful to people on low-sodium diets.
Aggarwala said the city has a few options.
Salt can be removed from water supplies through reverse osmosis systems, though the technology is expensive and requires a lot of energy. The city also could mix Croton water with less salty water from its other two watersheds. But the commissioner said that would not be a solution for the more than a dozen municipalities north of New York City that draw water from the Croton system.
City officials believe reducing the use of road salt locally is the most sensible option. That could involve persuading state and local road crews to use alternatives to salt, or sensors on plows to gauge road surface temperatures, or shutting off the applicators when plows make U-turns or K turns.
State Sen. Pete Harckham, who represents the area, called the new report alarming, but not surprising given a number of community wells taken offline due to high chloride levels. The Democrat is sponsoring bills that would address the road salt issue, including one that would study the issue in the Croton watershed.
“State agencies, local governments, everyone needs to come together on this,” he said, “because this is a real challenge.”
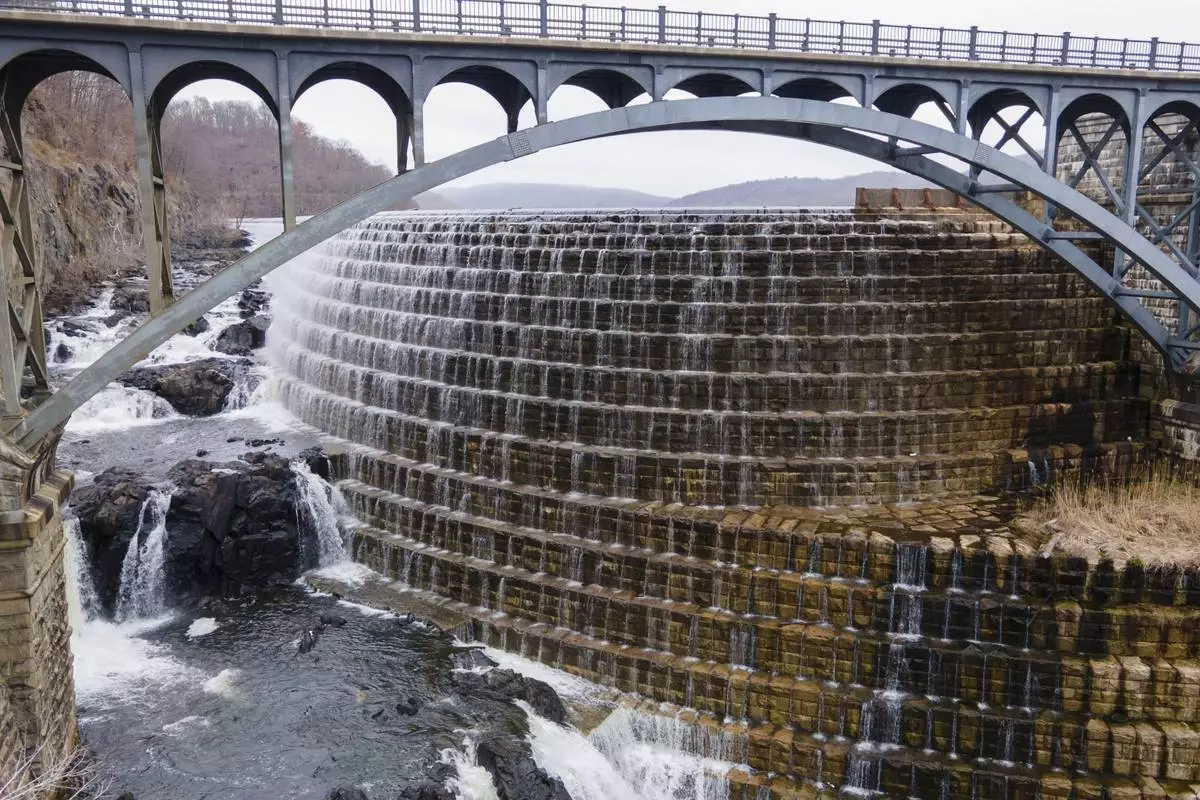

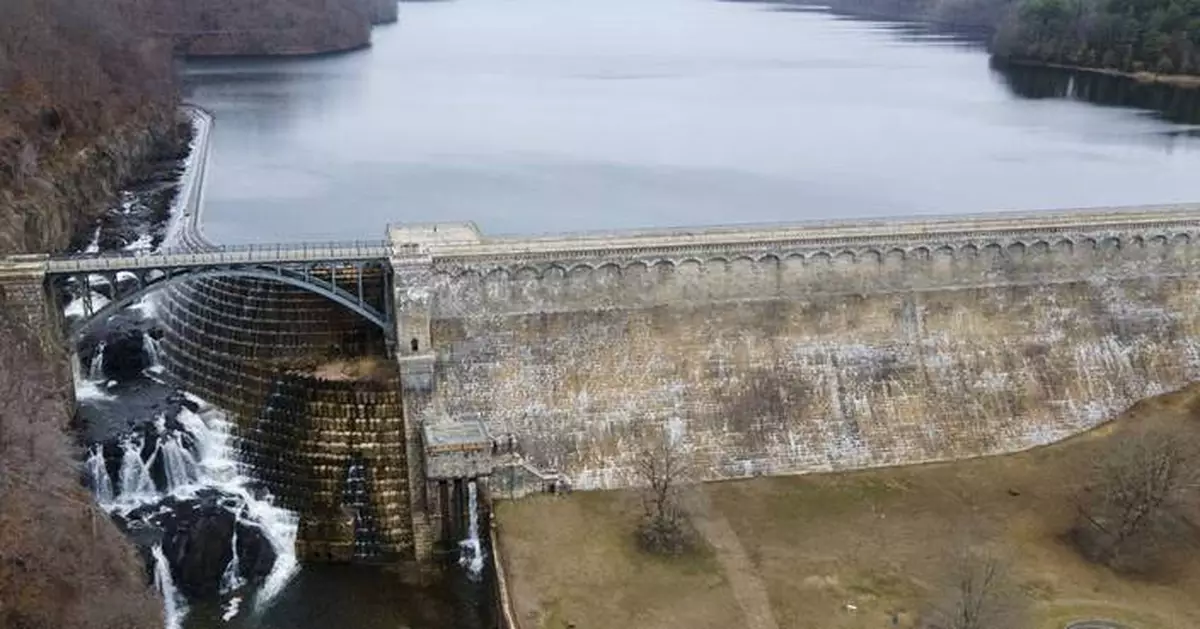
The New Croton Dam and the New Croton Reservoir that supplies part of New York City's drinking water is seen in Cortlandt, N.Y., on Thursday, March 20, 2025. (AP Photo/Ted Shaffrey)
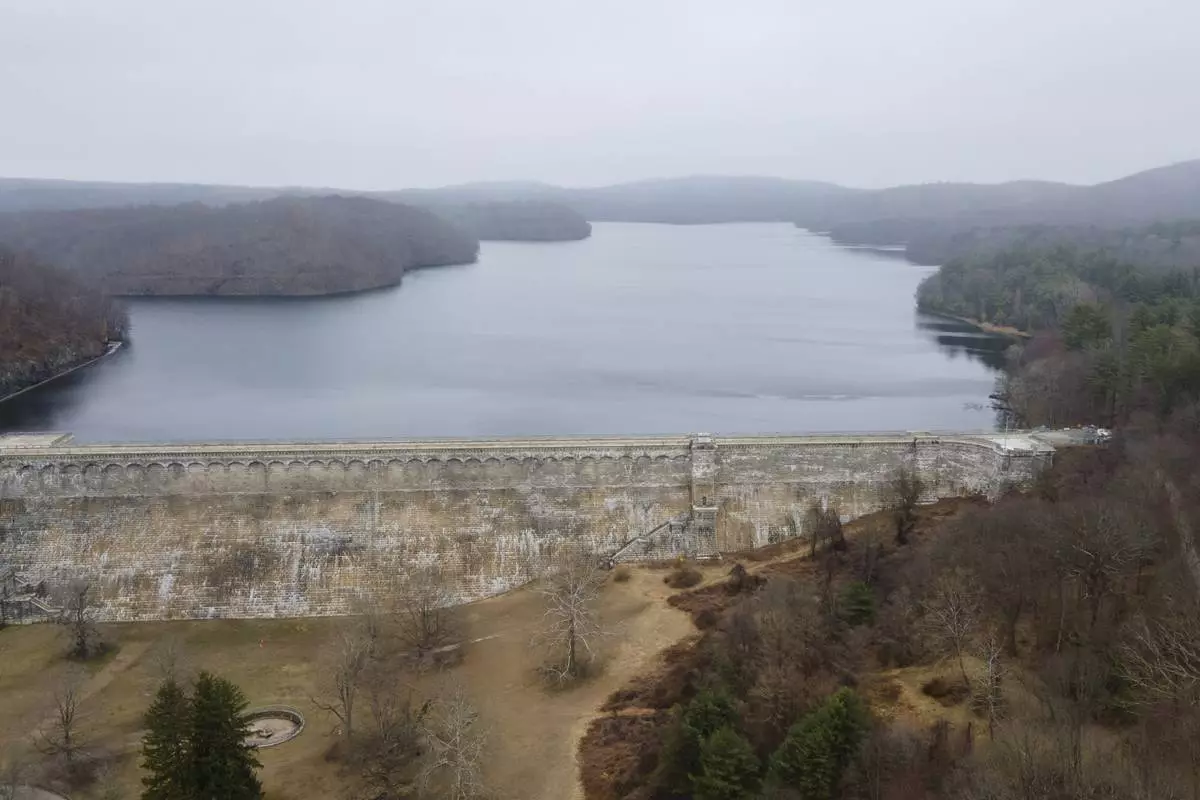

The New Croton Dam and the New Croton Reservoir that supplies part of New York City's drinking water is seen in Cortlandt, N.Y., on Thursday, March 20, 2025. (AP Photo/Ted Shaffrey)

The New Croton Reservoir that supplies part of New York City's drinking water is seen in Cortlandt, N.Y., on Thursday, March 20, 2025. (AP Photo/Ted Shaffrey)
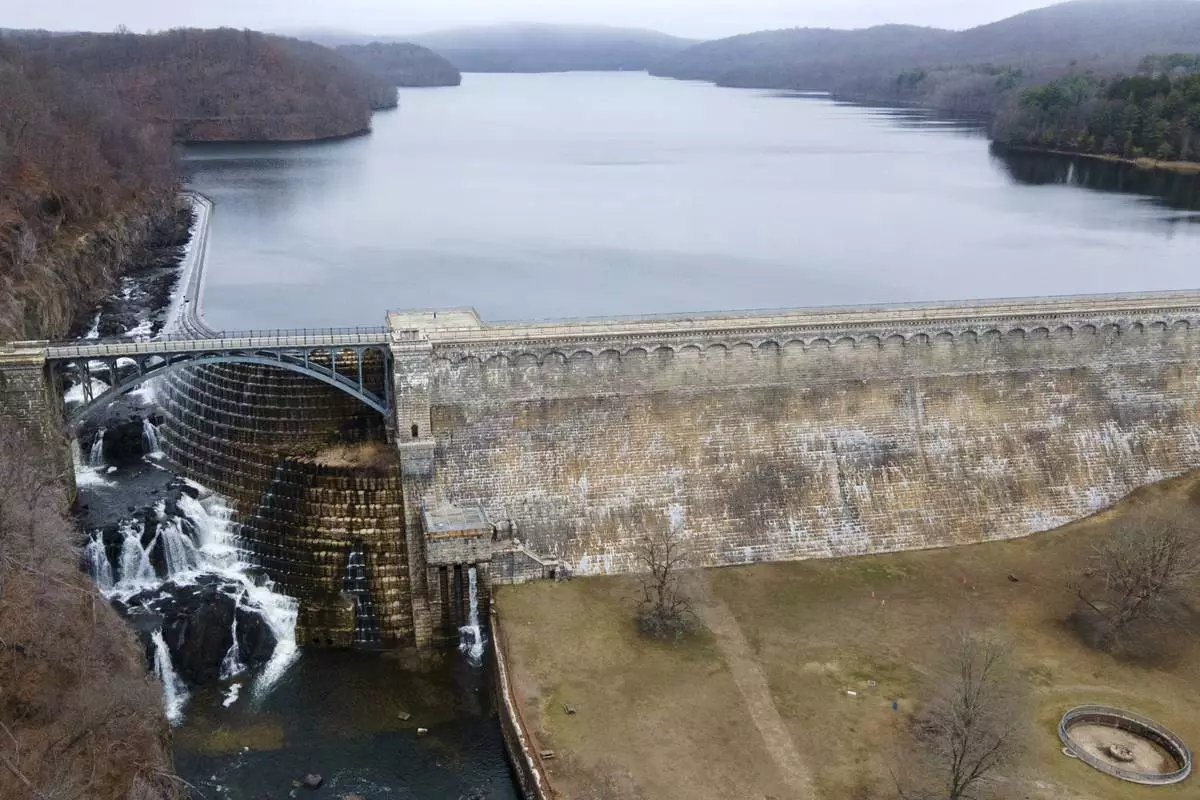

The New Croton Dam and the New Croton Reservoir that supplies part of New York City's drinking water is seen in Cortlandt, N.Y., on Thursday, March 20, 2025. (AP Photo/Ted Shaffrey)
ROME (AP) — Pope Francis will be released from the hospital on Sunday, after 38 days battling a life-threatening case of pneumonia in both lungs, his doctors said.
Gemelli medical director Dr. Sergio Alfieri said Saturday that Francis will require at least two months of rest and rehabilitation as he continues recovering back at the Vatican.
Francis was admitted to Gemelli hospital on Feb. 14 after a bout of bronchitis worsened. He later developed a life-threatening case of pneumonia.
Pope Francis ’ doctors provided their first in-person update on the pontiff’s condition in a month, in a sign that he has made good and steady progress in his battle against double pneumonia.
The Saturday evening briefing is the first since Feb. 21, a week after the 88-year-old Francis was brought to Gemelli hospital. He subsequently experienced several respiratory crises that landed him in critical condition, though he has since stabilized.
In another development, the Vatican announced that Francis would appear on Sunday morning to bless faithful from his 10th floor suite at the hospital. While Francis released an audio message on March 6 and the Vatican distributed a photo of him March 16, Sunday’s blessing will be the first live appearance since Francis was admitted on Feb. 14 for what has become the longest hospitalization of his 12-year papacy.
The Argentine pope, who has chronic lung disease, is prone to respiratory problems in winter and had part of one lung removed as a young man, was admitted after a bout of bronchitis worsened.
Doctors first diagnosed a complex bacterial, viral and fungal respiratory tract infection and soon thereafter, pneumonia in both lungs. Blood tests showed signs of anemia, low blood platelets and the onset of kidney failure, all of which later resolved after two blood transfusions.
The most serious setbacks began on Feb. 28, when Francis experienced an acute coughing fit and inhaled vomit, requiring he use a noninvasive mechanical ventilation mask to help him breathe. He suffered two more respiratory crises in the following days, which required doctors manually aspirate the mucus, at which point he began sleeping with the ventilation mask at night to help his lungs clear the accumulation of fluids.
At no point did he lose consciousness, and doctors reported he was alert and cooperative.
Over the past two weeks, he has stabilized and registered slight improvements, the Vatican press office has reported. He no longer needs to wear the ventilation mask at night, and is cutting back his reliance on high flows of supplemental oxygen during the day.
Associated Press religion coverage receives support through the AP’s collaboration with The Conversation US, with funding from Lilly Endowment Inc. The AP is solely responsible for this content.
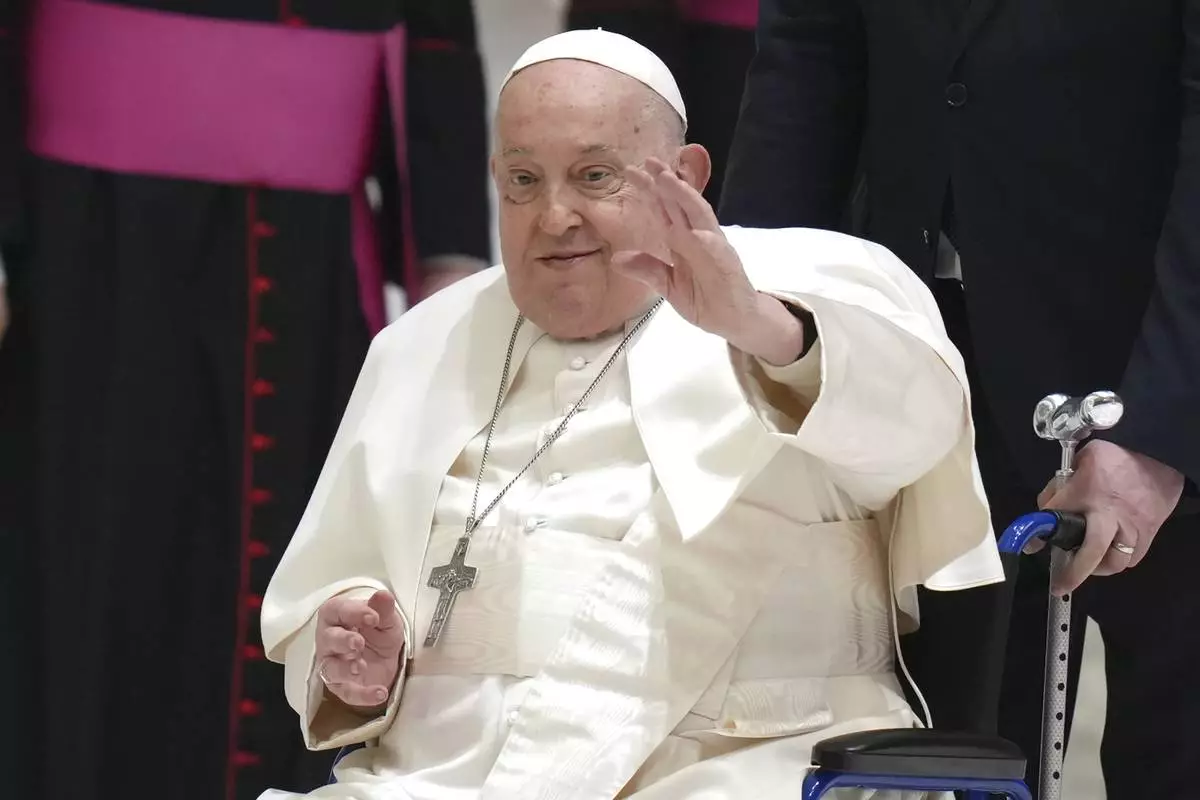

FILE - Pope Francis waves as he arrives for his weekly general audience in the Paul VI Hall, at the Vatican, Wednesday, Feb. 12, 2025. (AP Photo/Alessandra Tarantino, File)
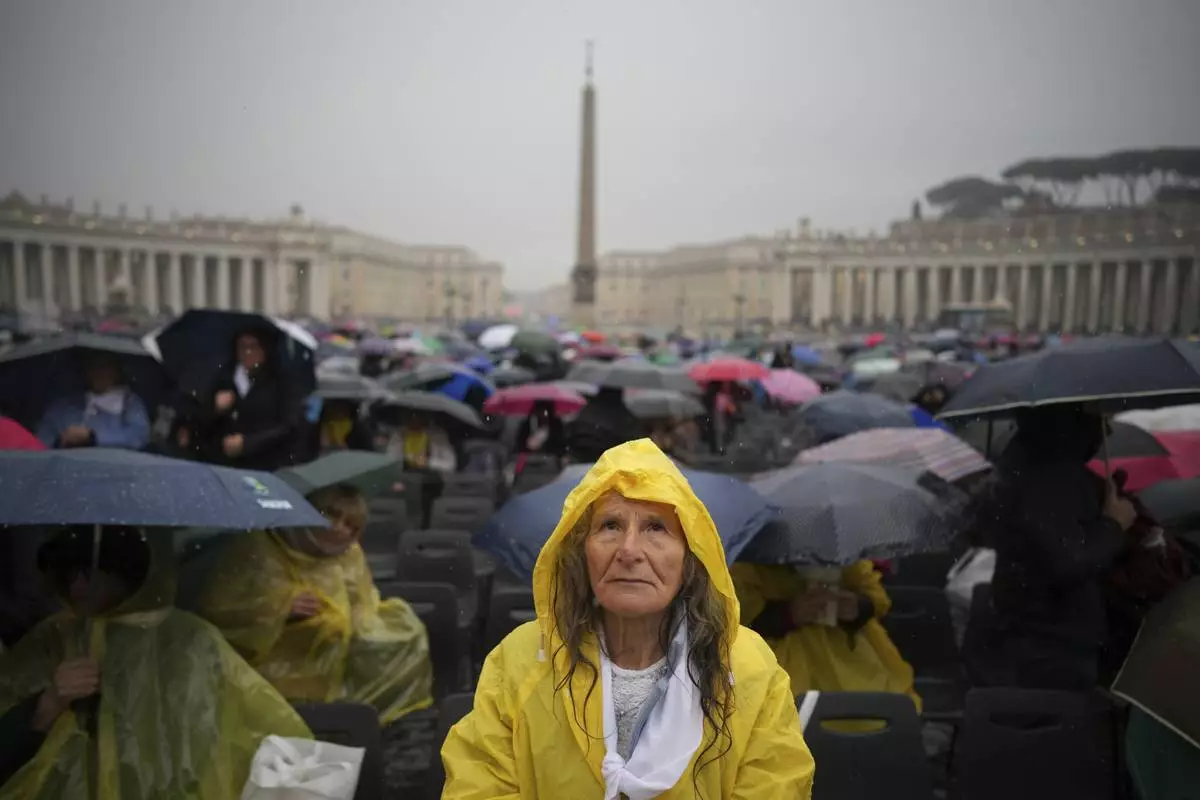

A participant in a mass for the jubilar pilgrims from Naples waits for the start of the celebration under pouring rain in St. Peter's Square at The Vatican, Saturday, March 22, 2025. (AP Photo/Andrew Medichini)
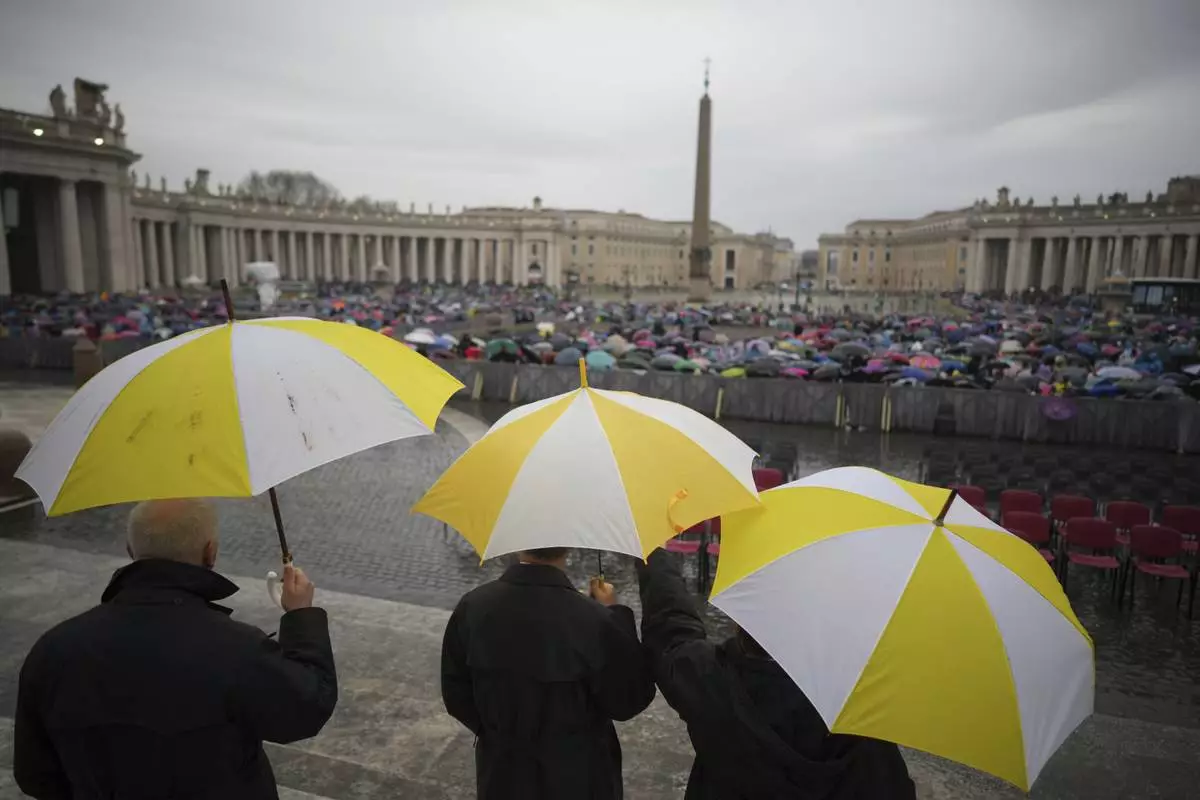

Participants in a mass for the jubilar pilgrims from Naples wait for the start of the celebration under pouring rain in St. Peter's Square at The Vatican, Saturday, March 22, 2025. (AP Photo/Andrew Medichini)

Participants in a mass for the jubilar pilgrims from Naples wait for the start of the celebration under pouring rain in St. Peter's Square at The Vatican, Saturday, March 22, 2025. (AP Photo/Andrew Medichini)
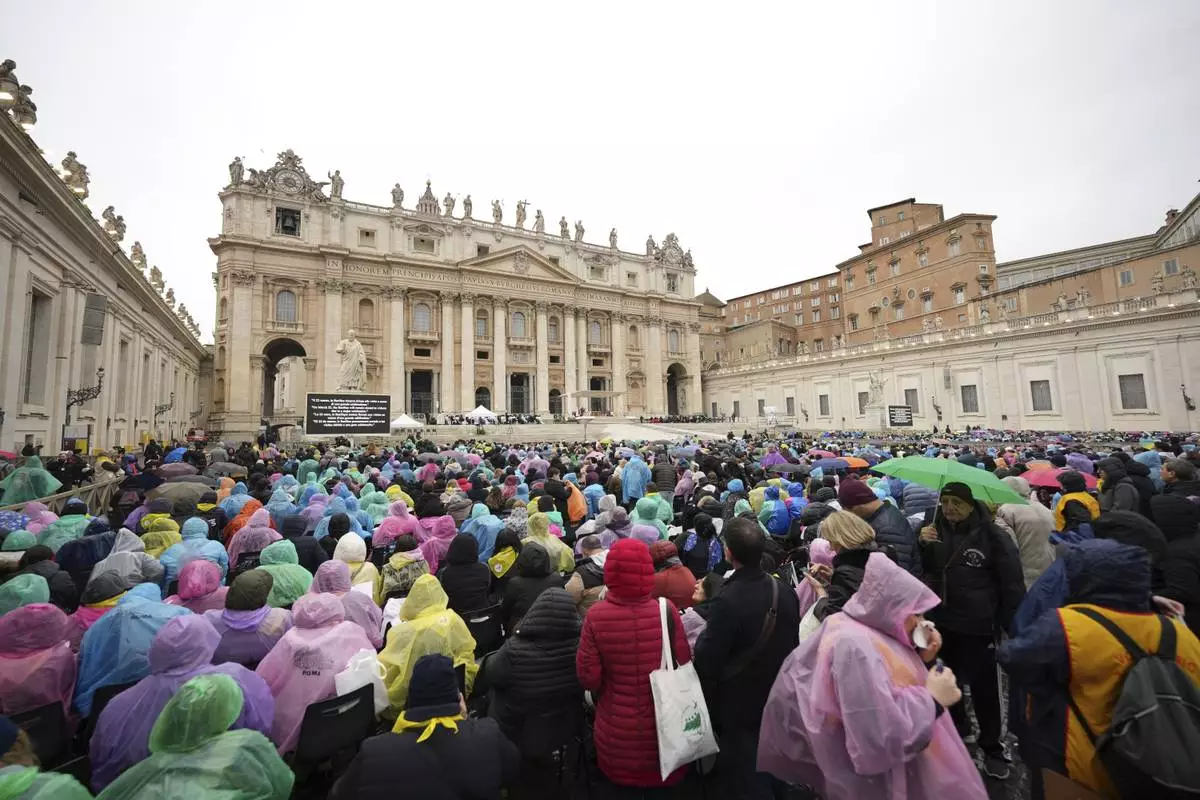

Participants in a mass for the jubilar pilgrims from Naples wait for the start of the celebration on a rainy day in St. Peter's Square at The Vatican, Saturday, March 22, 2025, while Pope Francis is being treated for bilateral pneumonia at Rome's Agostino Gemelli Polyclinic since Feb. 14. (AP Photo/Andrew Medichini)
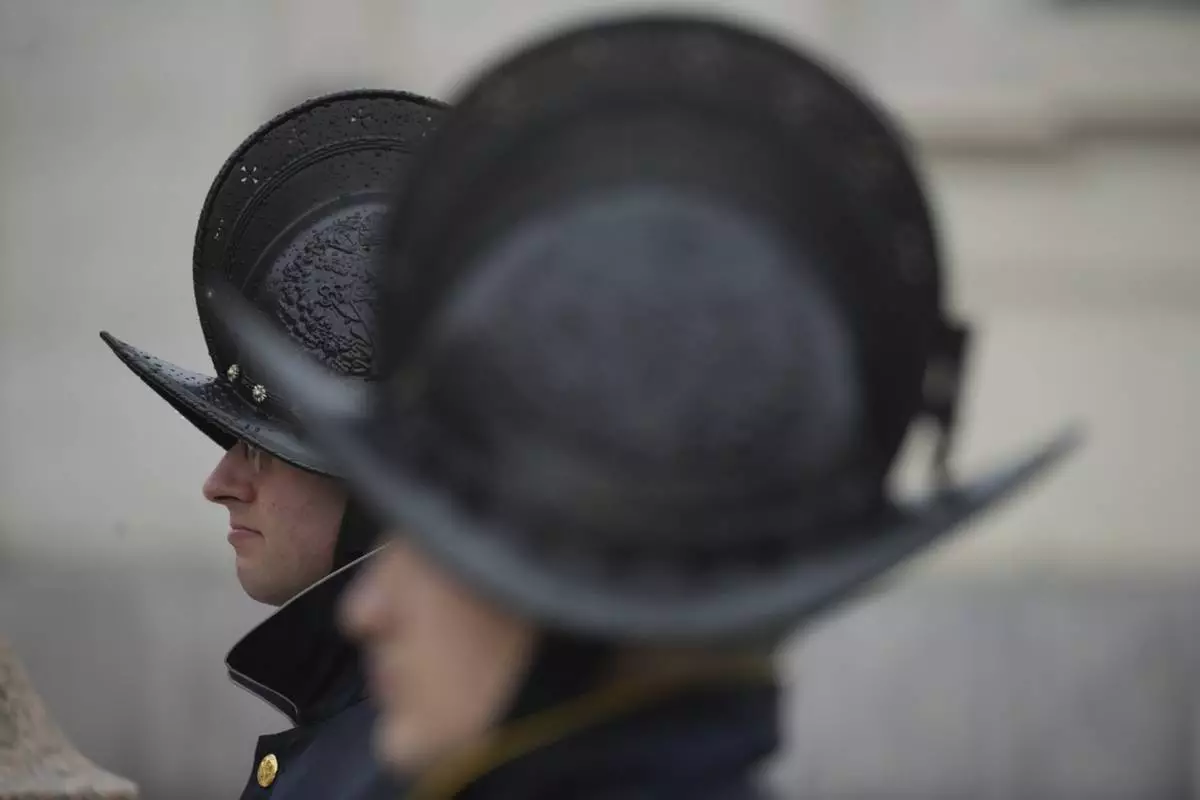

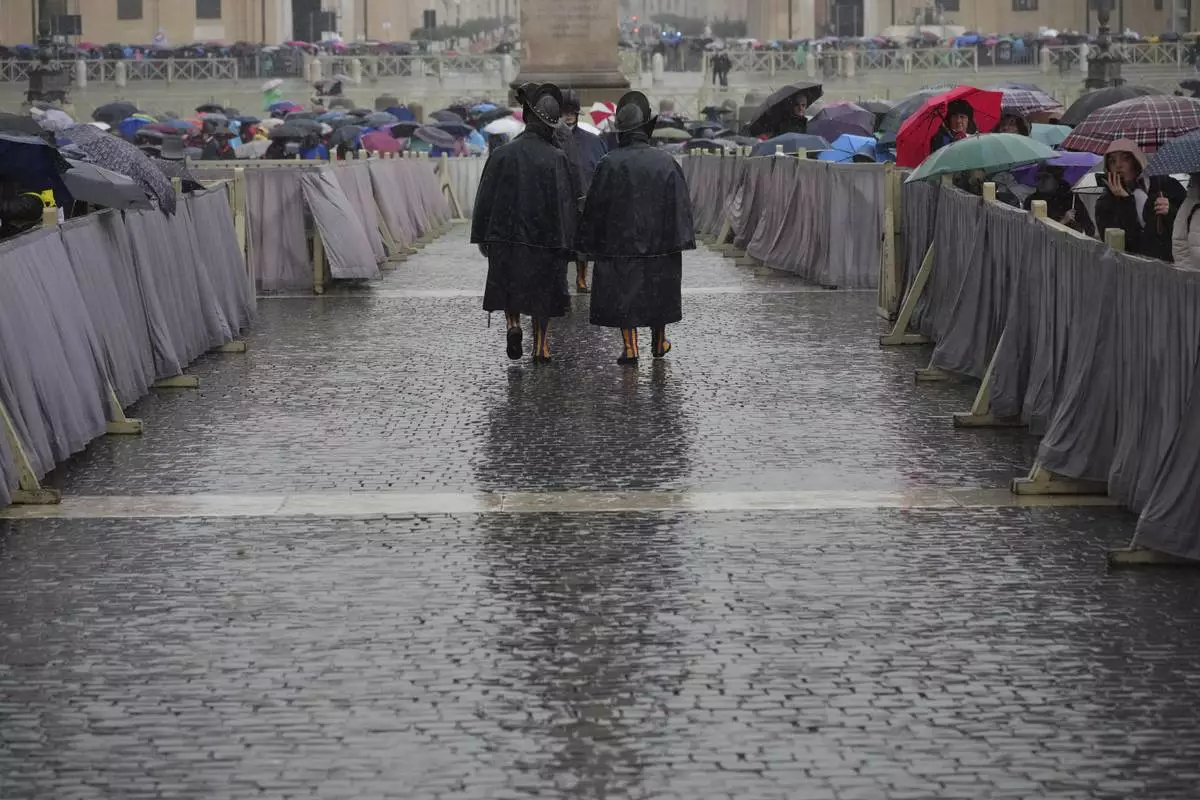
Pontifical Swiss Guards patrol during a mass for the jubilar pilgrims from Naples wait for the start of the celebration on a rainy day in St. Peter's Square at The Vatican, Saturday, March 22, 2025, while Pope Francis is being treated for bilateral pneumonia at Rome's Agostino Gemelli Polyclinic since Feb. 14. (AP Photo/Andrew Medichini)
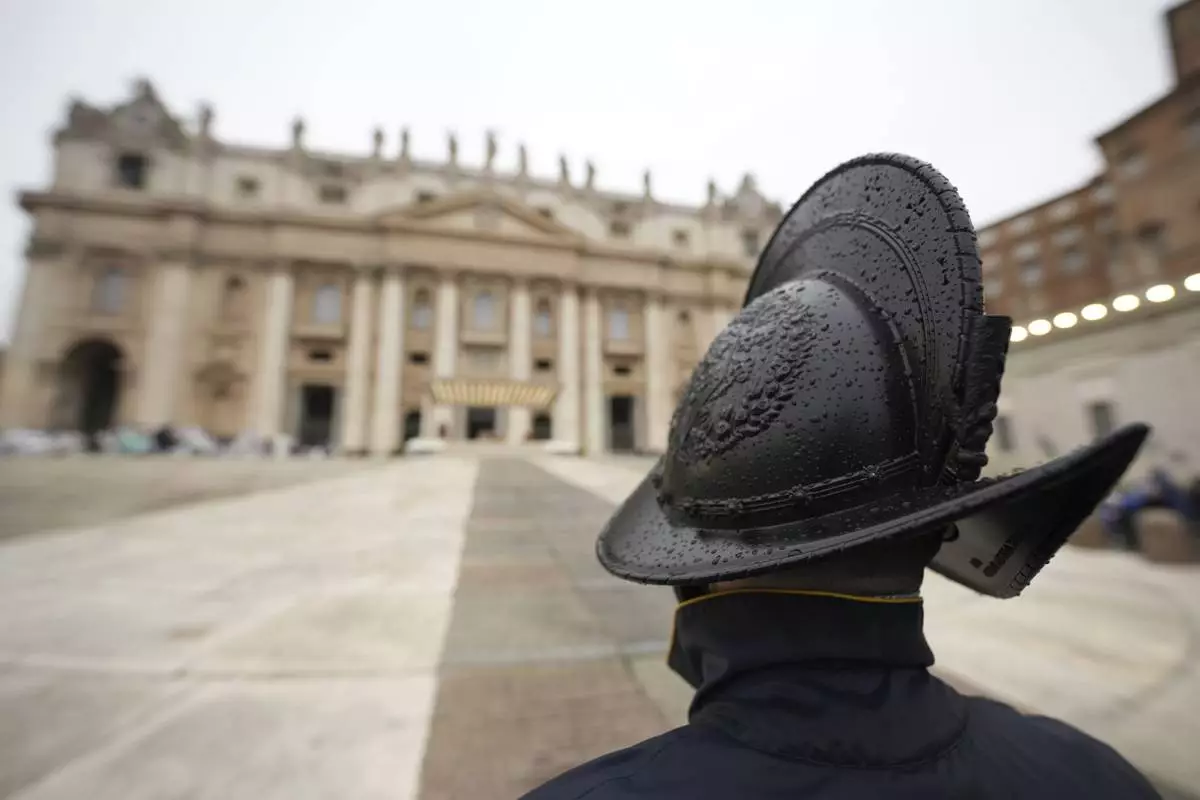

Pontifical Swiss Guards patrol during a mass for the jubilar pilgrims from Naples wait for the start of the celebration on a rainy day in St. Peter's Square at The Vatican, Saturday, March 22, 2025, while Pope Francis is being treated for bilateral pneumonia at Rome's Agostino Gemelli Polyclinic since Feb. 14. (AP Photo/Andrew Medichini)
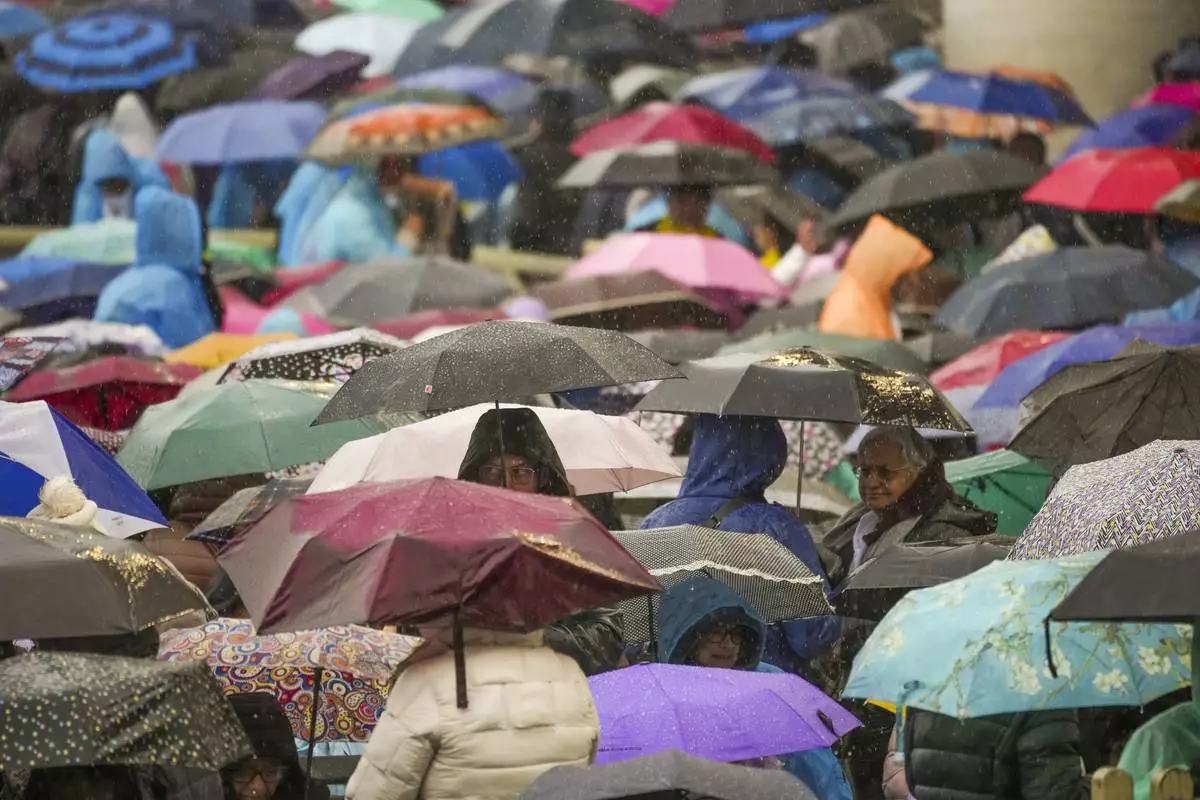

Participants in a mass for the jubilar pilgrims from Naples wait for the start of the celebration under pouring rain in St. Peter's Square at The Vatican, Saturday, March 22, 2025. (AP Photo/Andrew Medichini)