MIAMI (AP) — For the MIT-educated physicist behind the torpedo bat, it's more about the talent of the players than their lumber at the plate.
The torpedo model — a striking design in which wood is moved lower down the barrel after the label and shapes the end a little like a bowling pin — became the talk of major league baseball over the weekend.
Click to Gallery
Cincinnati Reds' Elly De La Cruz hits a two-run home run in the seventh inning of a baseball game against the Texas Rangers, Monday, March 31, 2025, in Cincinnati. (AP Photo/Kareem Elgazzar)
New York Yankees' Austin Wells watches his home run during the first inning of a baseball game against the Milwaukee Brewers, Saturday, March 29, 2025, in New York. (AP Photo/Angelina Katsanis)
New York Yankees' J.C. Escarra bats during the seventh inning of a baseball game against the Milwaukee Brewers, Saturday, March 29, 2025, in New York. (AP Photo/Angelina Katsanis)
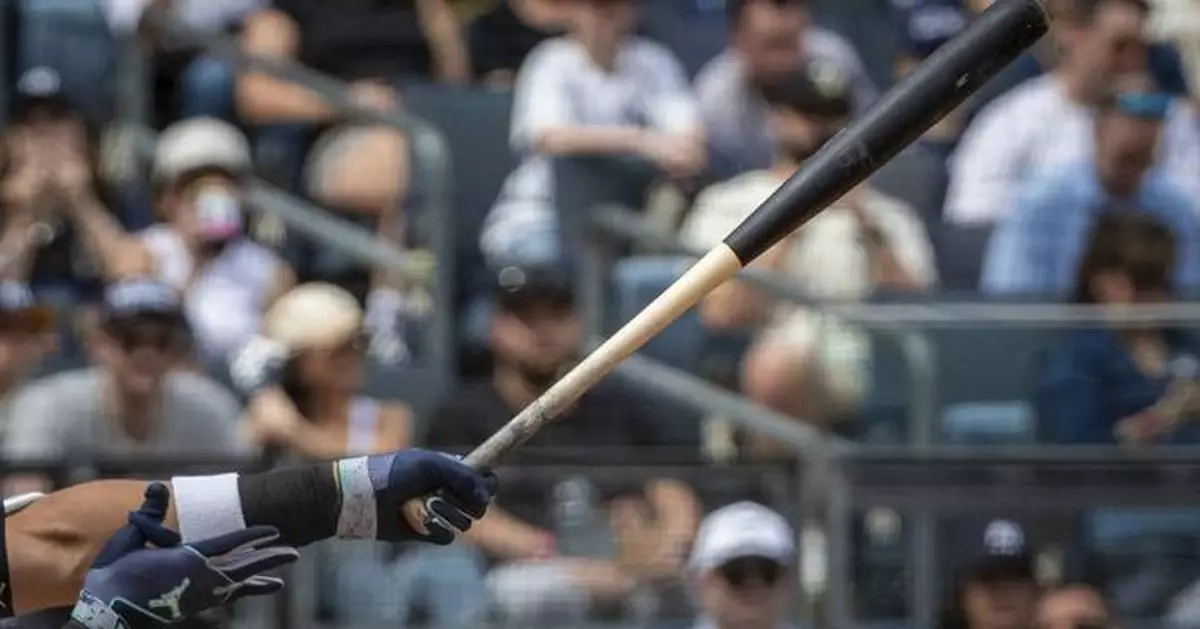
New York Yankees' Anthony Volpe bats with one of the team's newly-made torpedo-shaped bats in a baseball game against the Milwaukee Brewers, Saturday, March 29, 2025, in New York. (AP Photo/Angelina Katsanis)
New York Yankees' Aaron Judge hits a home run with one of the team's newly-made torpedo-shaped bats in a baseball game against the Milwaukee Brewers, Saturday, March 29, 2025, in New York. (AP Photo/Angelina Katsanis)
The New York Yankees hit a team-record nine homers that traveled a combined 3,695 feet on Saturday. Paul Goldschmidt, Cody Bellinger, Austin Wells, Anthony Volpe and Jazz Chisholm Jr. all went deep using a torpedo bat. New York's 15 homers through the first three games matched the 2006 Detroit Tigers for the most in major league history.
Cincinnati Reds shortstop Elly De La Cruz used a torpedo bat for a game for the first time on Monday night. He hit his first two homers of the season and finished with a career-high seven RBIs in a 14-3 victory over Texas.
“At the end of the day it’s about the batter not the bat,” said Aaron Leanhardt, a former physics professor at the University of Michigan who is being credited with the design. “It’s about the hitter and their hitting coaches. I’m happy to always help those guys get a little bit better but ultimately it’s up to them to put good swings and grind it out every day. So, credit to those guys.”
The 23-year-old De La Cruz said the torpedo bat felt good. Asked if he planned to use it again after his performance, he just laughed in response.
Leanhardt, 48, a field coordinator for the Miami Marlins, said the origin of the bat dates to 2023, when he worked for the Yankees. He said several versions were tested that didn’t create the desired effect.
Leanhardt was approached by major league and minor league players early in the design stage, seeking information on the bats.
"I’ll let the players always talk about their own experiences. I’m not going to drag anyone into this,” Leanhardt said Monday. “But there were definitely guys on the major league side and on the minor league side in 2023 that were definitely asking me questions and offering design advice and demoing them.”
Leanhardt said the past couple of days had been “surreal.” Some of Miami's players joked around with him as he answered questions from the media before their game against the New York Mets.
“The industry as a whole was probably a little bit more aware of this maybe than you guys were,” Leanhardt said. “Guys have been asking me about it. Guys have been wanting to swing them.”
Bat manufacturer Victus Sports dropped off a batch of torpedo bats for the Phillies just before first pitch of their home opener on Monday. Alec Bohm grabbed one, took about five swings and decided to use one.
His logic seemed sound: Look how it might have aided the Yankees.
“You see a team hit 20 homers and you’re gonna try it,” Bohm said. “It didn’t work.”
Bohm managed just one single with his new lumber. He noted it “felt just like a normal bat” and wasn’t sure if he would swing with a torpedo again any time soon.
“It’s a bat. It’s different,” he said. “It’ll probably run its course.”
Victus and Marucci Sports started selling torpedo bats online on Monday. Each company highlighted its offerings on social media. Chandler Bats also had new torpedo bats on its website.
Milwaukee Brewers outfielder Christian Yelich said he didn't feel like the bats had any effect on their opening series against the Yankees.
“I think they have a lot of really good players. That’s probably the biggest factor in how that went,” he said.
Mets manager Carlos Mendoza said shortstop Francisco Lindor used a similar bat in their series at Houston. He got the models late in spring training.
“Nothing new for us,” Mendoza said. “This is something that every team, every player continues to look for an edge and find ways to improve within the margins. And this is a perfect example.”
AP MLB: https://apnews.com/hub/mlb
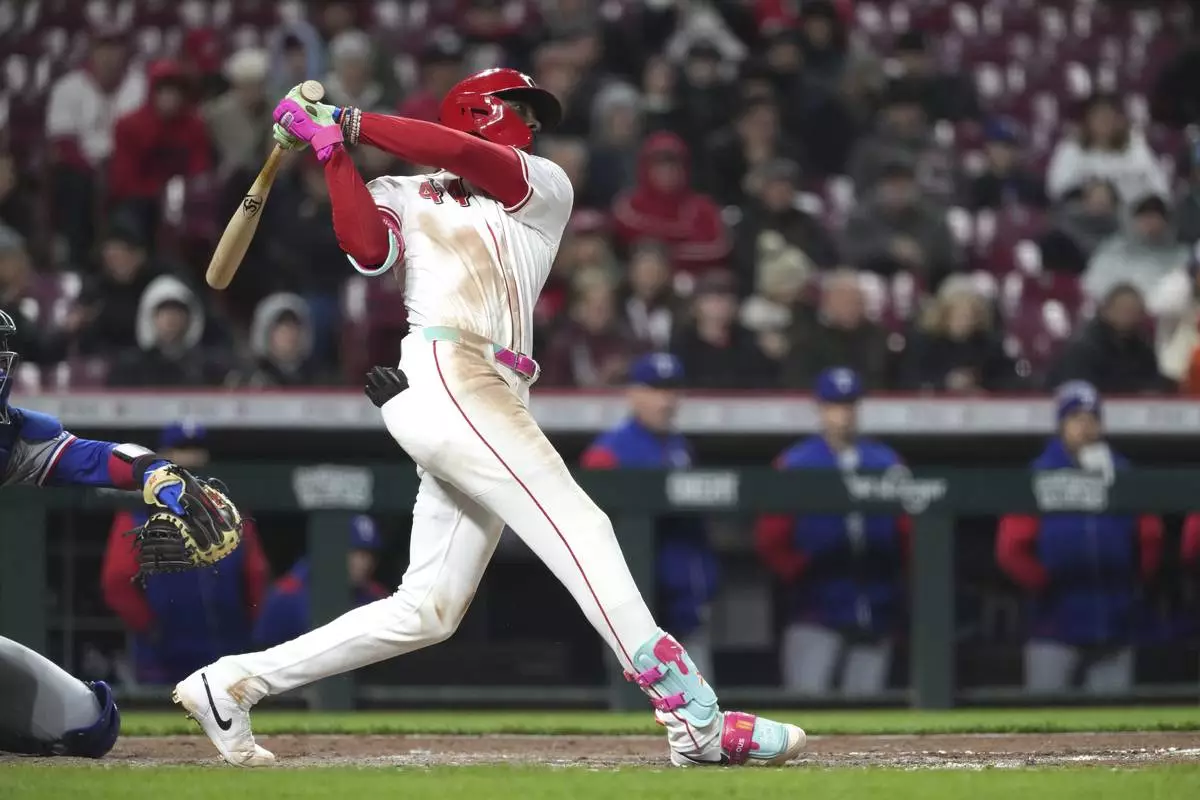

Cincinnati Reds' Elly De La Cruz hits a two-run home run in the seventh inning of a baseball game against the Texas Rangers, Monday, March 31, 2025, in Cincinnati. (AP Photo/Kareem Elgazzar)
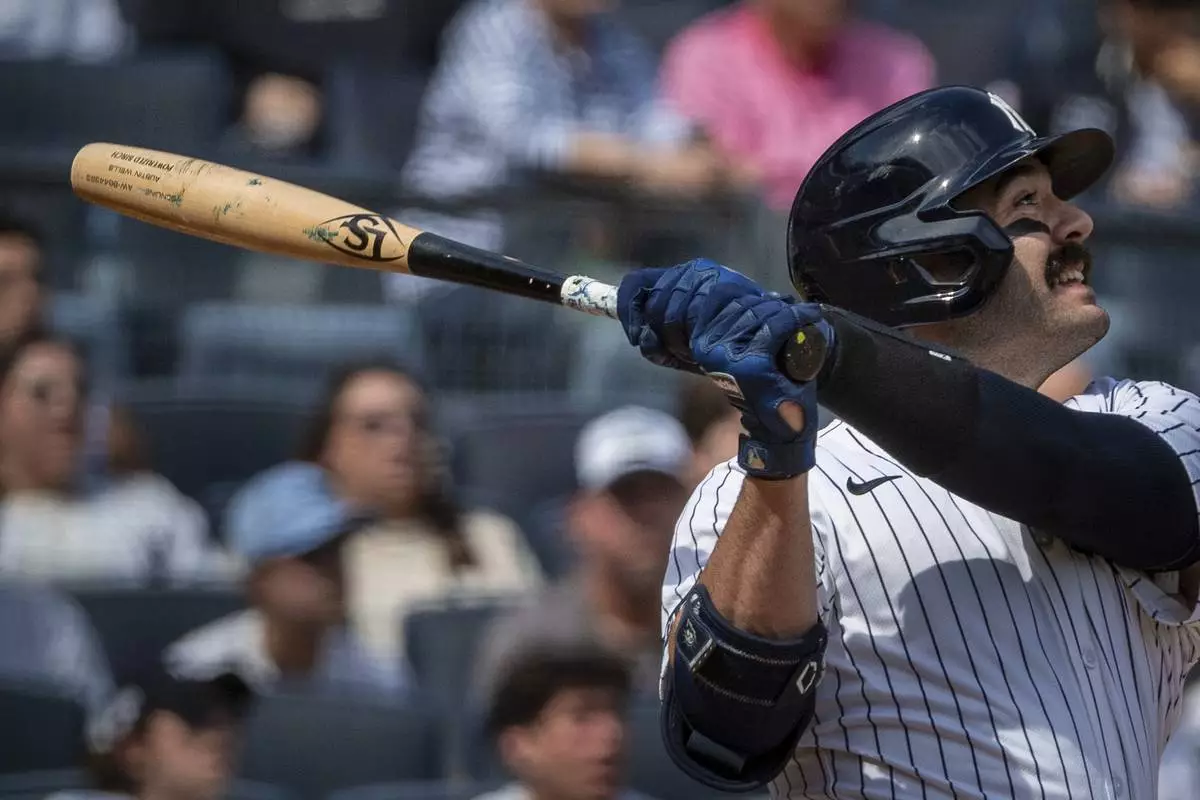

New York Yankees' Austin Wells watches his home run during the first inning of a baseball game against the Milwaukee Brewers, Saturday, March 29, 2025, in New York. (AP Photo/Angelina Katsanis)
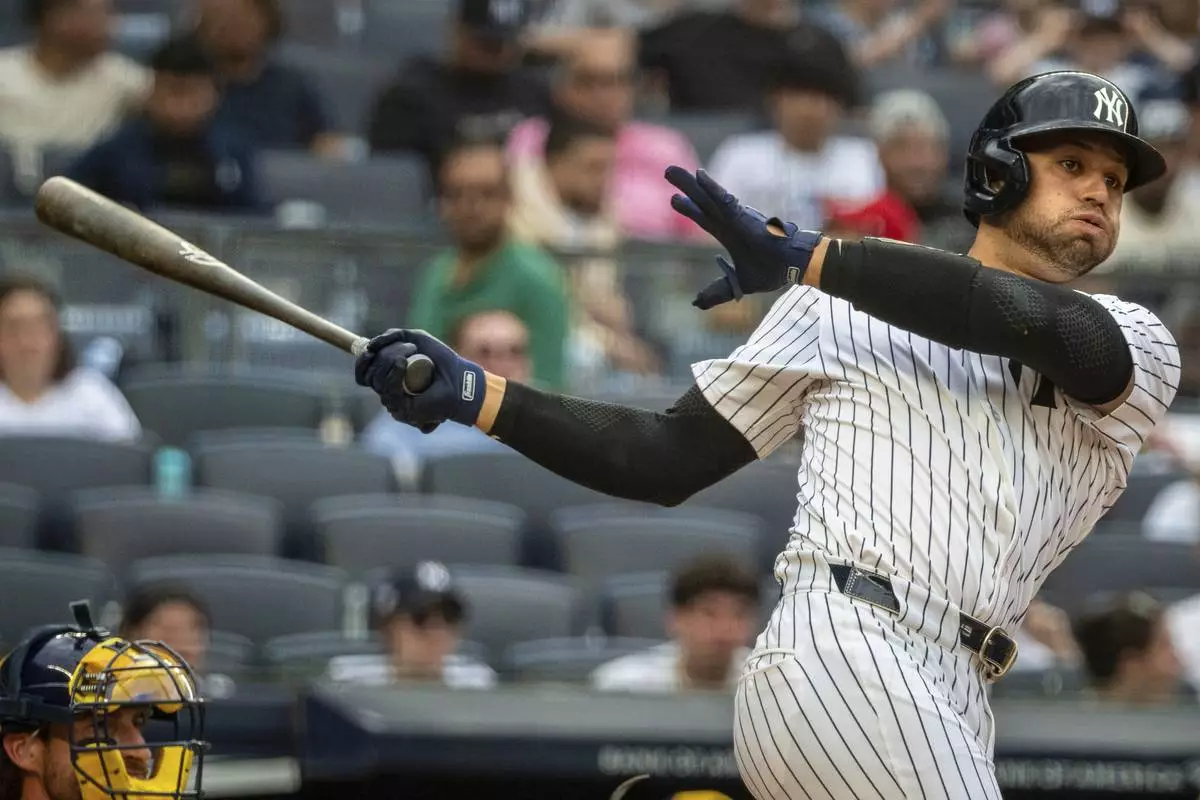

New York Yankees' J.C. Escarra bats during the seventh inning of a baseball game against the Milwaukee Brewers, Saturday, March 29, 2025, in New York. (AP Photo/Angelina Katsanis)
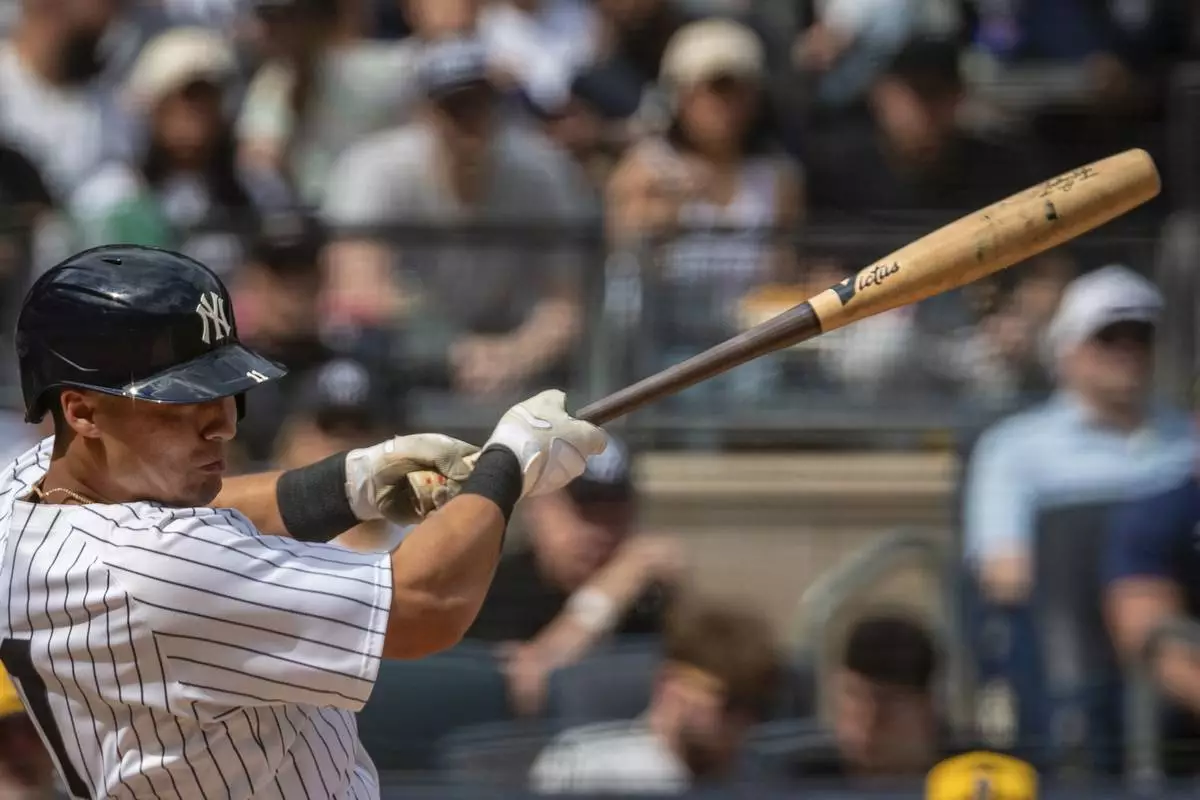

New York Yankees' Anthony Volpe bats with one of the team's newly-made torpedo-shaped bats in a baseball game against the Milwaukee Brewers, Saturday, March 29, 2025, in New York. (AP Photo/Angelina Katsanis)
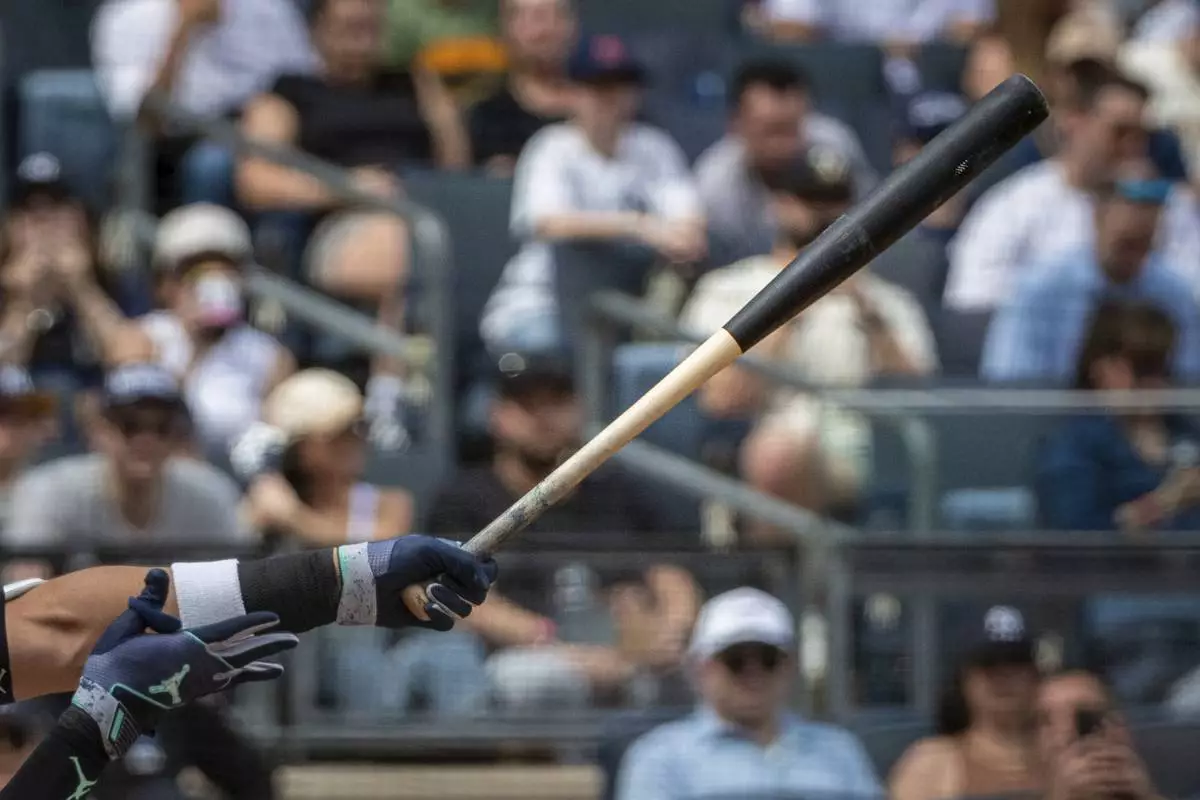

New York Yankees' Aaron Judge hits a home run with one of the team's newly-made torpedo-shaped bats in a baseball game against the Milwaukee Brewers, Saturday, March 29, 2025, in New York. (AP Photo/Angelina Katsanis)
TEL AVIV, Israel (AP) — Israel has dramatically expanded its footprint in the Gaza Strip since relaunching its war against Hamas last month. It now controls more than 50% of the territory and is squeezing Palestinians into shrinking wedges of land.
The largest contiguous area the army controls is around the Gaza border, where the military has razed Palestinian homes, farmland and infrastructure to the point of uninhabitability, according to Israeli soldiers and rights groups. This military buffer zone has doubled in size in recent weeks.
Israel has depicted its tightening grip as a temporary necessity to pressure Hamas into releasing the remaining hostages taken during the Oct. 7, 2023, attack that started the war. But the land Israel holds, which includes a corridor that divides the territory's north from south, could be used for wielding long-term control, human rights groups and Gaza experts say.
Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said last week that even after Hamas is defeated, Israel will keep security control in Gaza and push Palestinians to leave.
The demolition close to the Israeli border and the systematic expansion of the buffer zone has been going on since the war began 18 months ago, five Israeli soldiers told The Associated Press.
“They destroyed everything they could, they shot everything that looks functioning ... (the Palestinians) will have nothing to come back, they will not come back, never,” a soldier deployed with a tank squad guarding the demolition teams said. He and four other soldiers spoke to the AP on condition of anonymity for fear of reprisals.
A report documenting the accounts of soldiers who were in the buffer zone was released Monday by Breaking The Silence, an anti-occupation veterans group. A handful of soldiers -- including some who also spoke to AP -- described watching the army turn the zone into a vast wasteland.
“Through widespread, deliberate destruction, the military laid the groundwork for future Israeli control of the area,” said the group.
Asked about the soldiers’ accounts, the Israeli army said it is acting to protect its country and especially to improve security in southern communities devastated by the Oct. 7 attack, in which some 1,200 people were killed and 251 taken hostage. The army said it does not seek to harm civilians in Gaza, and that it abides by international law.
In the early days of the war, Israeli troops forced Palestinians from communities near the border and destroyed the land to create a buffer zone more than a kilometer (0.62 miles) deep, according to Breaking The Silence.
Its troops also seized a swath of land across Gaza known as the Netzarim Corridor that isolated the north, including Gaza City, from the rest of the narrow, coastal strip, home to more than 2 million people.
When Israel resumed the war last month, it doubled the size of the buffer zone, pushing it as far as 3 kilometers (1.8 miles) into Gaza in some places, according to a map issued by the military.
The buffer zone and the Netzarim Corridor make up at least 50% of the strip, said Yaakov Garb, a professor of environmental studies at Ben Gurion University, who has been examining Israeli-Palestinian land use patterns for decades.
Last week, Netanyahu said Israel intends to create another corridor that slices across southern Gaza, cutting off the city of Rafah from the rest of the territory. Israel’s control of Gaza is even greater taking into account areas where it recently ordered civilians to evacuate ahead of planned attacks.
Hundreds of thousands of Palestinians used to live in the land that now makes up Israel's buffer zone, an area that was key to Gaza's agricultural output.
Satellite images show once dense neighborhoods turned to rubble, as well as nearly a dozen new Israeli army outposts since the ceasefire ended.
When the ceasefire was announced in January, Nidal Alzaanin went back to his home in Beit Hanoun in northern Gaza. His property stood on the edge of the buffer zone and lay in ruins.
All that remains is a photo of him and his wife on their wedding day, a drawing of his son’s face on a porcelain plate and the carcass of a 150-year-old sycamore tree planted by his great-grandfather. His greenhouse was reduced to twisted scraps of metal.
The 55-year-old farmer pitched a tent in the rubble, hoping to rebuild his life. But when Israel resumed its campaign and seized his land, he was again uprooted.
“It took 20 years to build a house and within five minutes they destroyed all my dreams and my children’s dreams,” he said from Gaza City, where he now shelters.
Israel’s bombardment and ground offensives throughout the war have left vast swaths of Gaza’s cities and towns destroyed. But the razing of property inside the buffer zone has been more methodical and extensive, soldiers said.
The five soldiers who spoke to the AP said Israeli troops were ordered to destroy farmland, irrigation pipes, crops and trees as well as thousands of buildings, including residential and public structures, so that militants had nowhere to hide.
Several soldiers said their units demolished more buildings than they could count, including large industrial complexes. A soda factory was leveled, leaving shards of glass and solar panels strewn on the ground.
The soldiers said the buffer zone had no marked boundaries, but that Palestinians who entered were shot at.
The soldier with the tank squad said an armored bulldozer flattened land creating a “kill zone” and that anyone who came within 500 meters of the tanks would be shot, including women and children.
Visibly shaken, he said many of the soldiers acted out of vengeance for the Oct. 7 attack.
“I came there because they kill us and now we’re going to kill them. And I found out that we’re not only killing them. We’re killing them, we’re killing their wives, their children, their cats, their dogs, and we destroyed their houses,” he said.
The army said its attacks are based on intelligence and that it avoids “as much as possible, harm to non-combatants.”
It is unclear how long Israel intends to hold the buffer zone and other territory inside Gaza.
In announcing the new corridor across southern Gaza, Netanyahu said Israel aims to pressure Hamas to release the remaining 59 hostages, of whom 35 are believed dead. He also said the war can only end when Hamas is destroyed and its leaders leave Gaza, at which point Israel would take control of security in the territory.
Then, Netanyahu said, Israel would implement U.S. President Donald Trump’s call to move Palestinians from Gaza, what Israel calls “voluntary emigration.”
Some Israel analysts say the purpose of the buffer zone isn’t to occupy Gaza, but to secure it until Hamas is dismantled. “This is something that any sane country will do with regard to its borders when the state borders a hostile entity,” said Kobi Michael, a senior researcher at two Israeli think tanks, the Institute for National Security Studies and the Misgav Institute.
But rights group say forcibly displacing people is a potential war crime and crime against humanity. Within Gaza’s buffer zones, specifically, it amounts to “ethnic cleansing,” because it was clear people would never be allowed to return, said Nadia Hardman, a researcher at Human Rights Watch.
Israel called the accusations baseless and said it evacuates civilians from combat areas to protect them.
Associated Press reporter Michael Biesecker contributed from Washington.
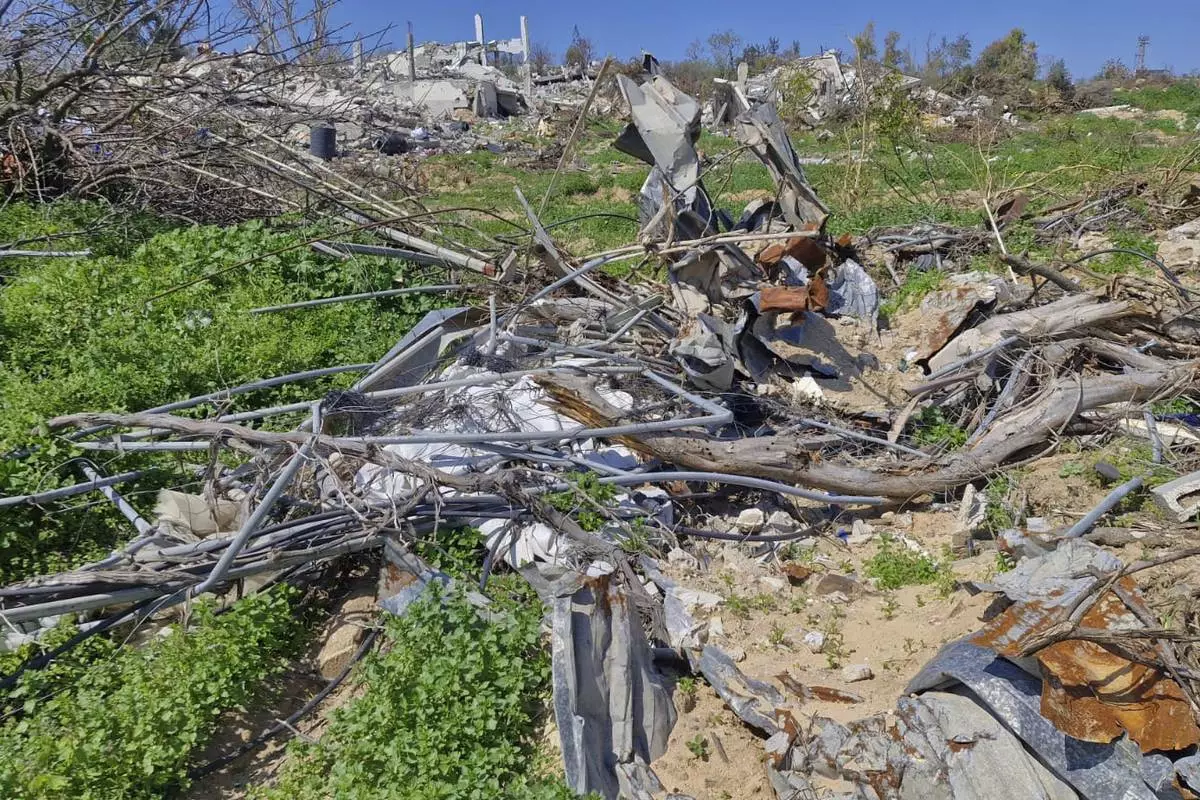

This photo provided by Palestinian Nidal Alzaanin, shows his destroyed greenhouse in Beit Hanoun, Gaza Strip, March, 2025. (AP Photo/Nidal Alzaanin)
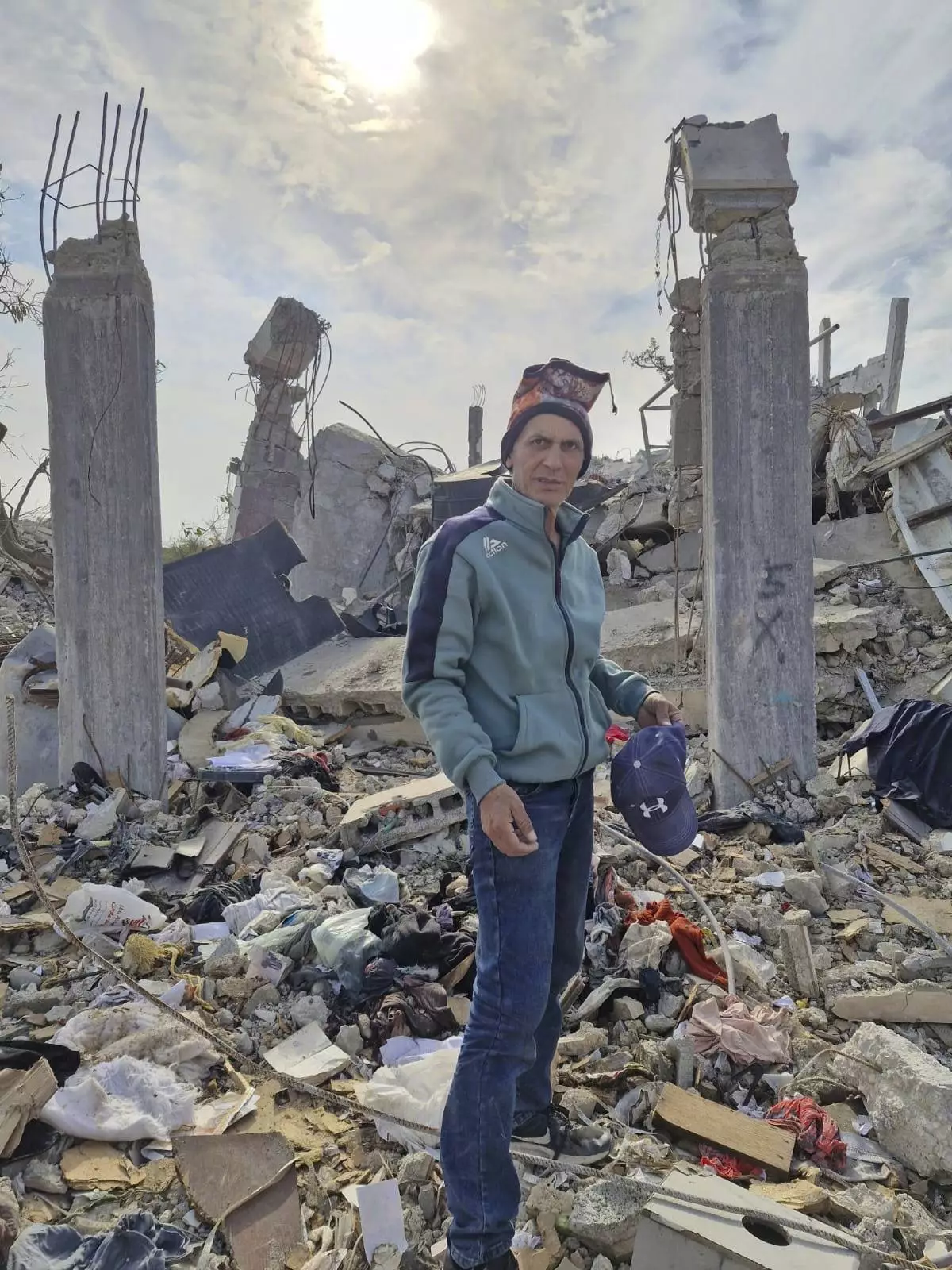

This photo provided by Palestinian Nidal Alzaanin, shows him standing in front of his demolished home in Beit Hanoun, Gaza Strip, March, 2025. (AP Photo)
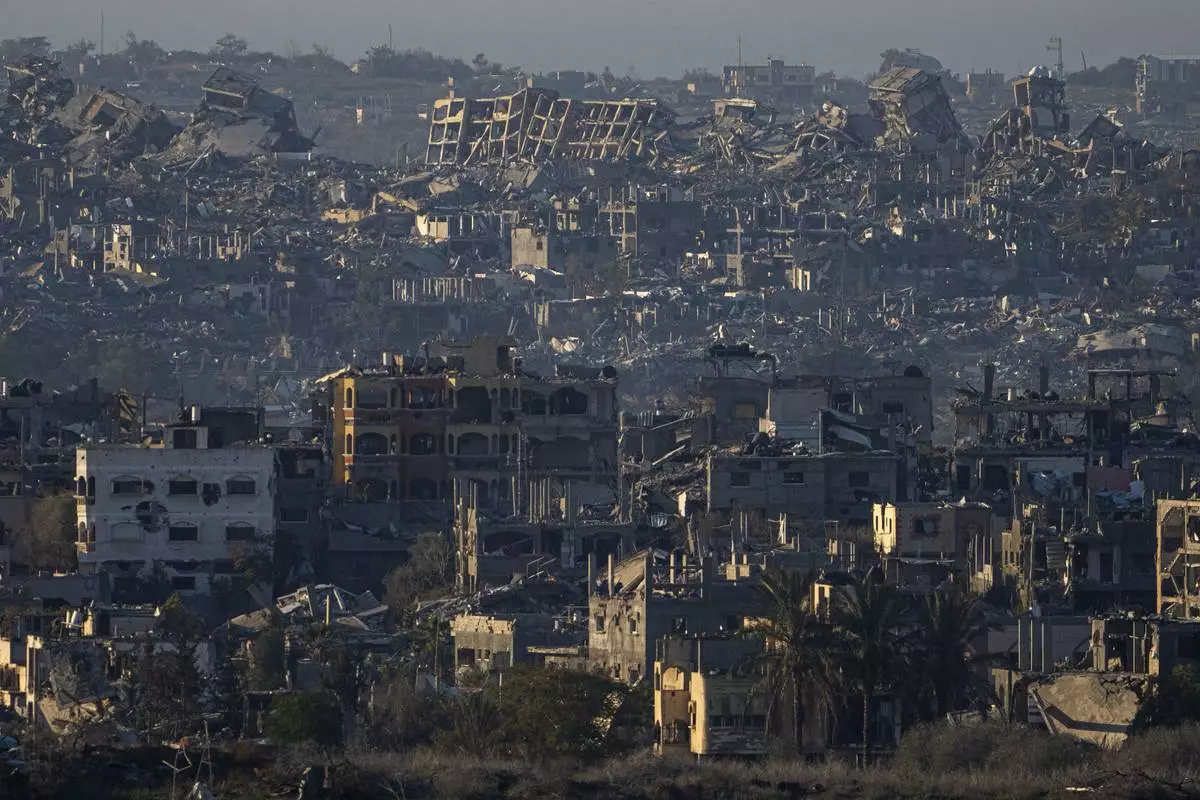

FILE - Destroyed buildings are seen inside the Gaza Strip from southern Israel, Jan. 13, 2025. (AP Photo/Ariel Schalit, File)
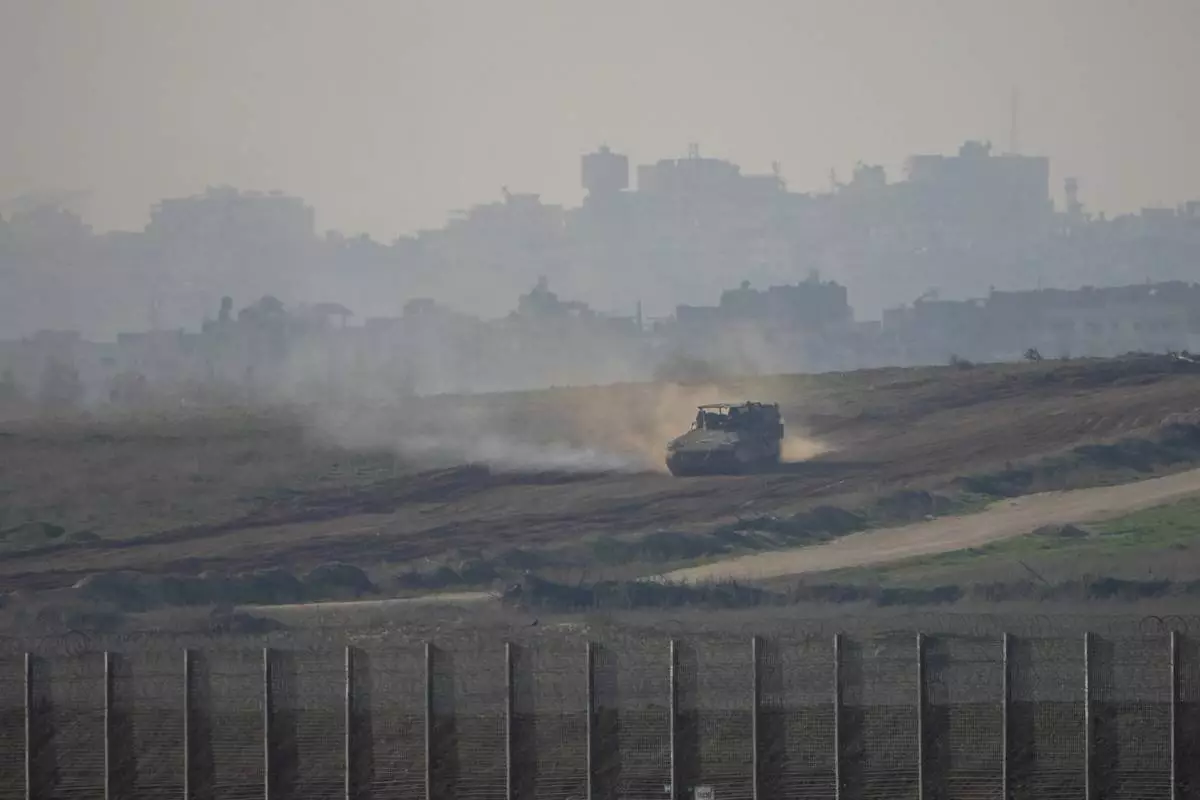

FILE - An Israeli army vehicle moves in the Gaza Strip as seen from southern Israel, Jan. 16, 2025. (AP Photo/Ariel Schalit, File)
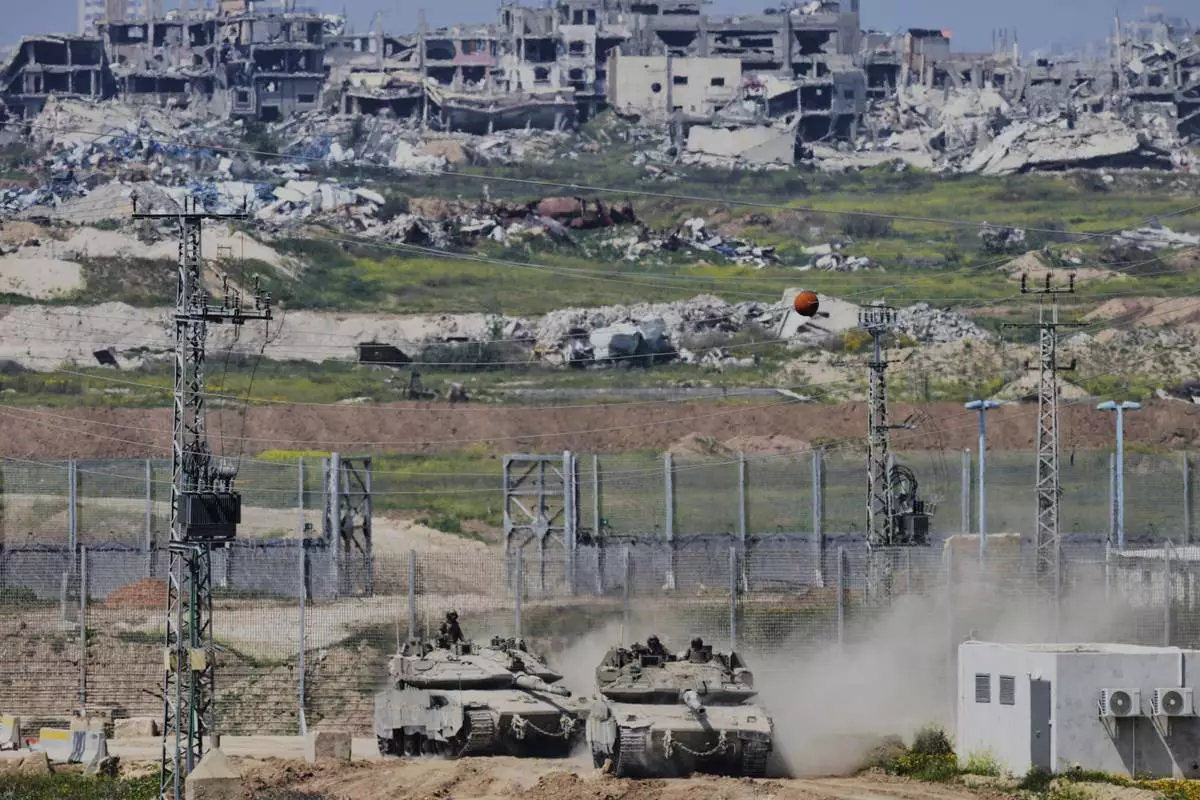

FILE - Israeli tanks maneuver along the border with north of the Gaza Strip, as seen from southern Israel, March 18, 2025. (AP Photo/Ohad Zwigenberg, File)
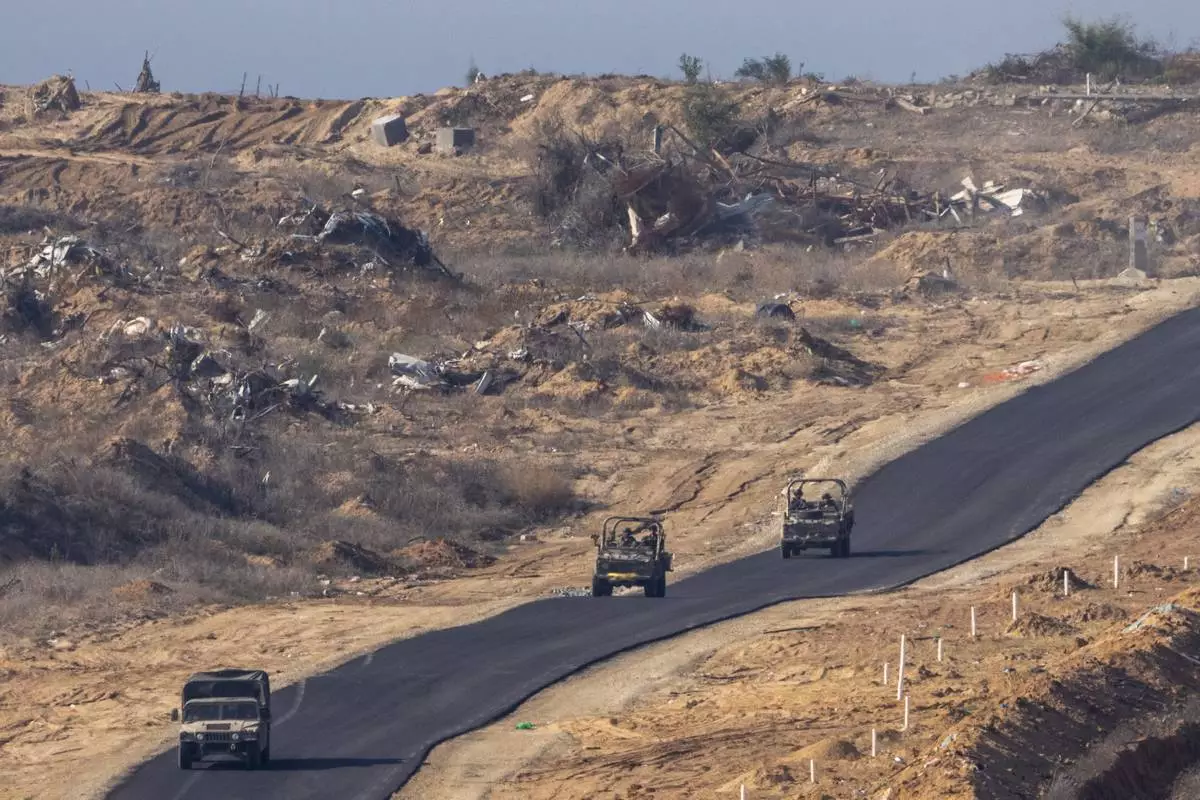

FILE - Israeli military vehicles move inside the Gaza Strip, as seen from southern Israel, Tuesday, Jan. 7, 2025. (AP Photo/Ariel Schalit, File)