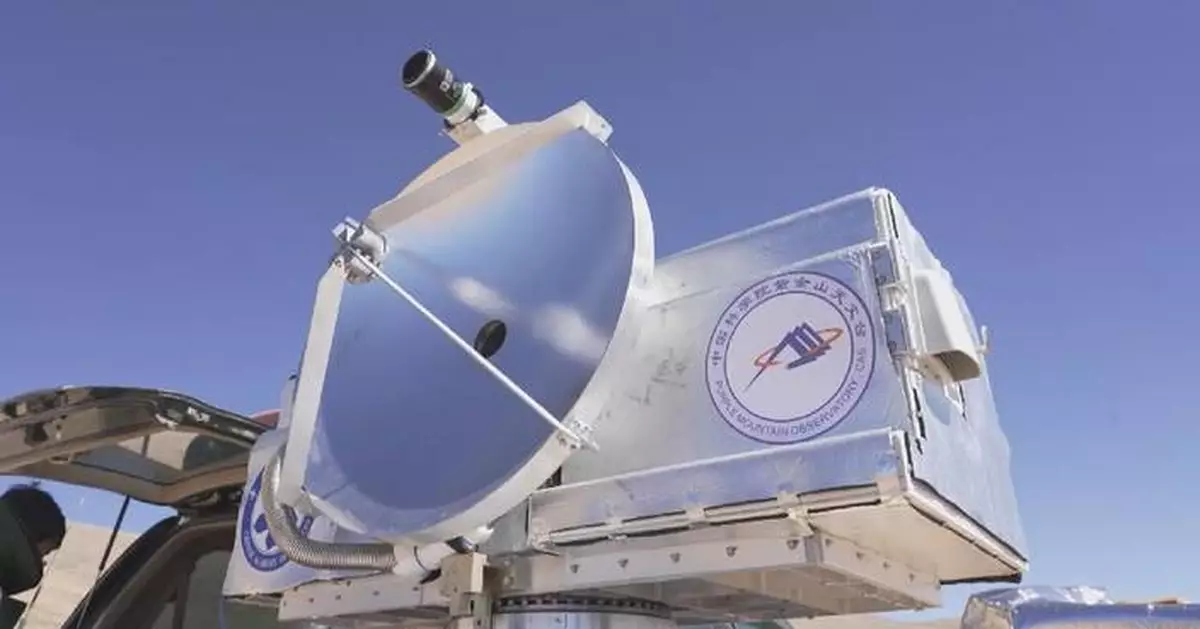
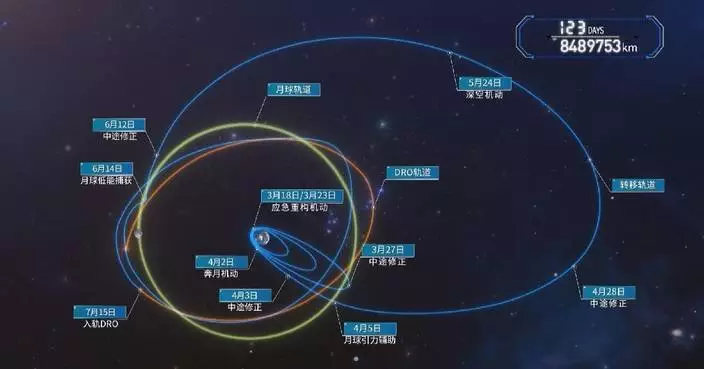
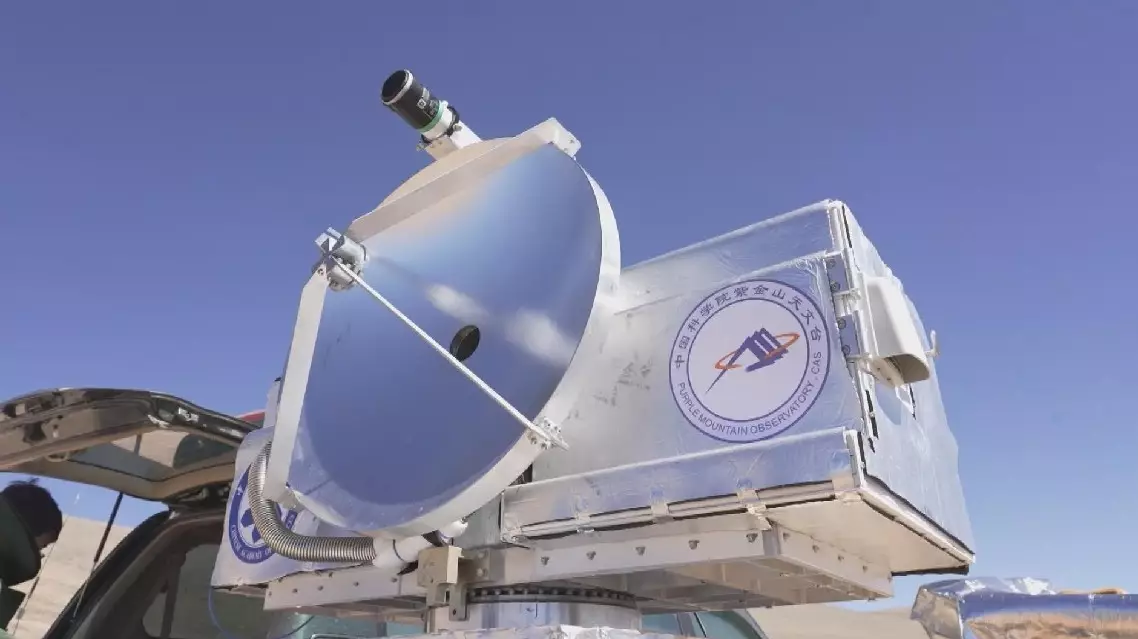
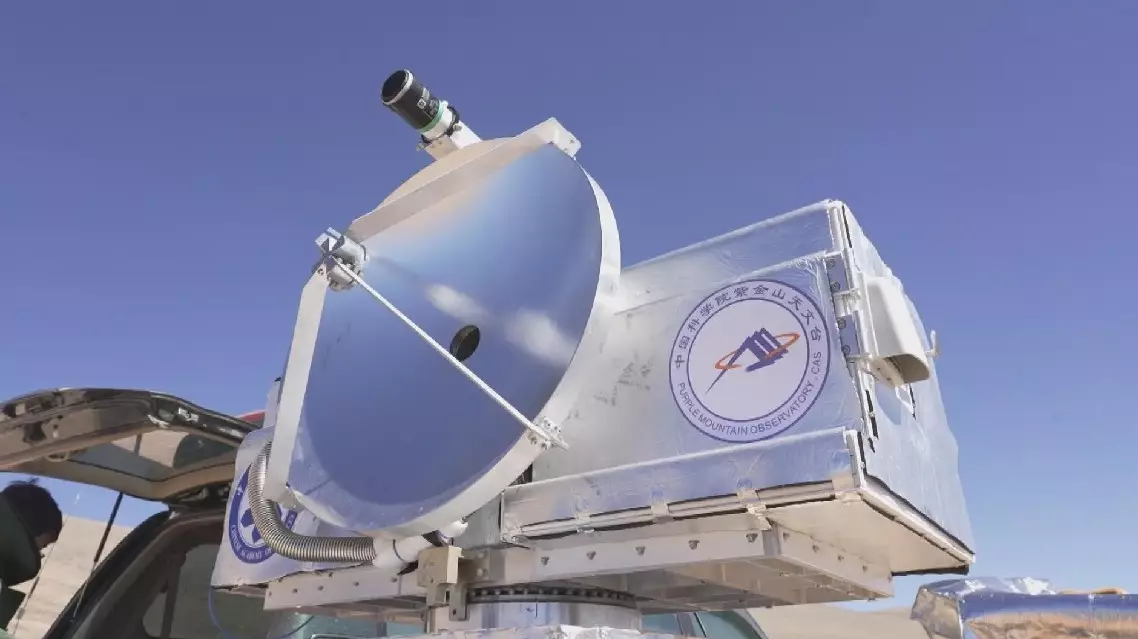
Chinese scientists have successfully transmitted high-definition video signals over kilometers using terahertz wireless communication technology, marking the world's first case to apply superconducting terahertz receivers to long-distance wireless communication systems.
Terahertz waves refer to electromagnetic waves with wavelengths between 3,000 and 30 micrometers, sitting between microwaves and optical infrared frequencies. Research into the terahertz range deepens the understanding of fundamental scientific questions in physics, astronomy, and information science. Applications for terahertz technology span various fields, including astronomical observation, biomedical science, and data transmission, with significant implications for cutting-edge research, national economic development, and security.
The experiment was carried out from Sept 27 to Oct 1 at the submillimeter-wave astronomical observation base at an altitude of over 4,000 meters located on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Researchers from the Purple Mountain Observatory under Chinese Academy of Sciences led the experiment with other teams.
"For example, if we see microwave communication as a two-lane road, then terahertz communication, due to its broader and richer spectrum resources, is like expanding that road to six or eight lanes. The significance of the superconducting detection technology we used this time lies in its high sensitivity. It's like having better-performing cars on this wider road, with almost no energy loss, allowing the signals to travel much farther," said Li Jing, researcher at the Purple Mountain Observatory.
This experiment has fully demonstrated the unique advantages of using superconducting receivers in terahertz communication, laying critical technical foundation for future space and air-to-ground high-capacity terahertz communication, as well as the construction of a multi-disciplinary platform at the submillimeter-wave observatory.

Chinese scientists achieve breakthrough in long-distance terahertz wireless communication

Chinese scientists achieve breakthrough in long-distance terahertz wireless communication