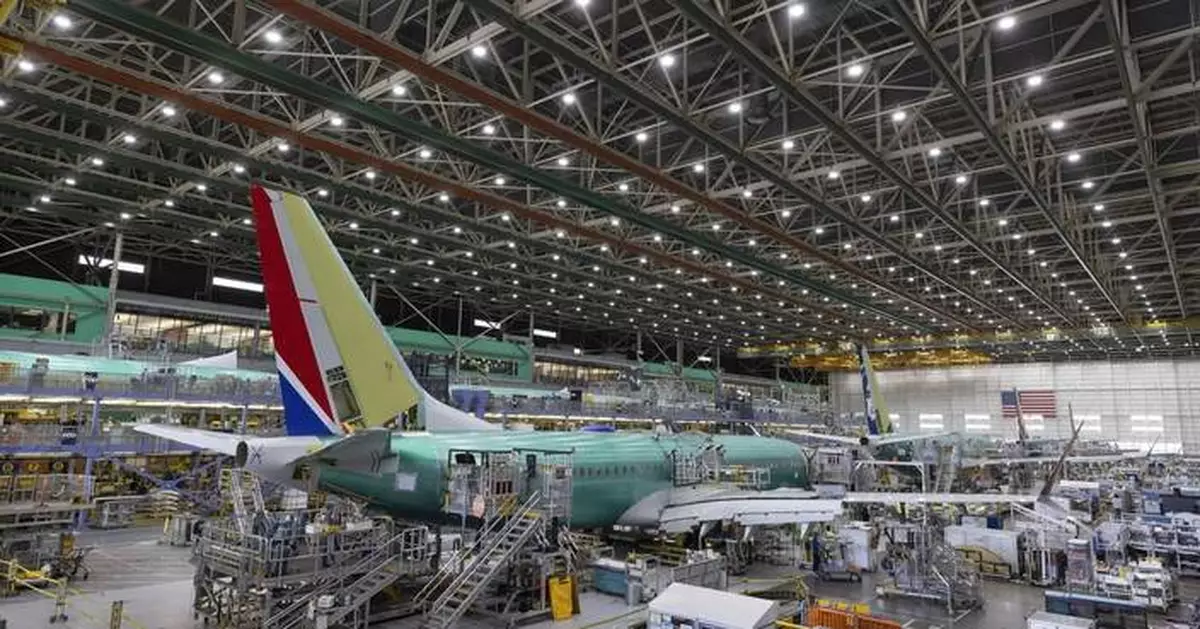
SEATTLE (AP) — Boeing said in a notice filed with Washington's Employment Security Department on Monday that it has so far laid off 2,199 workers in the state, among job cuts that will eventually total about 17,000 across the company.
The aerospace giant announced in October that it planned to cut about 10% of its workforce in the coming months as it struggles to recover from financial and regulatory troubles as well as a strike by its machinists that lasted nearly two months.
The planned cuts include workers at Boeing facilities across the country, from Washington to Missouri to Arizona to South Carolina, The Seattle Times reported. They also appeared to impact workers in all three of Boeing’s divisions: commercial airplanes, defense and global services.
Before the layoff notices delivered last week, Boeing had 66,000 workers in Washington.
Among the layoffs so far are notices that went out last week to more than 400 members of Boeing's professional aerospace labor union, the Society of Professional Engineering Employees in Aerospace, or SPEEA. The workers will remain on the payroll through mid-January.
Boeing’s unionized machinists began returning to work earlier this month following the strike.
The strike strained Boeing’s finances. But CEO Kelly Ortberg said on an October call with analysts that it did not cause the layoffs, which he described as a result of overstaffing.
Boeing, based in Arlington, Virginia, has been in financial trouble since two crashes of its 737 Max jetliner killed 346 people in 2018 and 2019. The company's fortunes and reputation took a further hit when a panel blew off the fuselage of an Alaska Airlines plane in January.
Production rates slowed to a crawl, and the Federal Aviation Administration capped production of the 737 MAX at 38 planes per month, a threshold Boeing had yet to reach when the machinists' strike halted assembly lines.
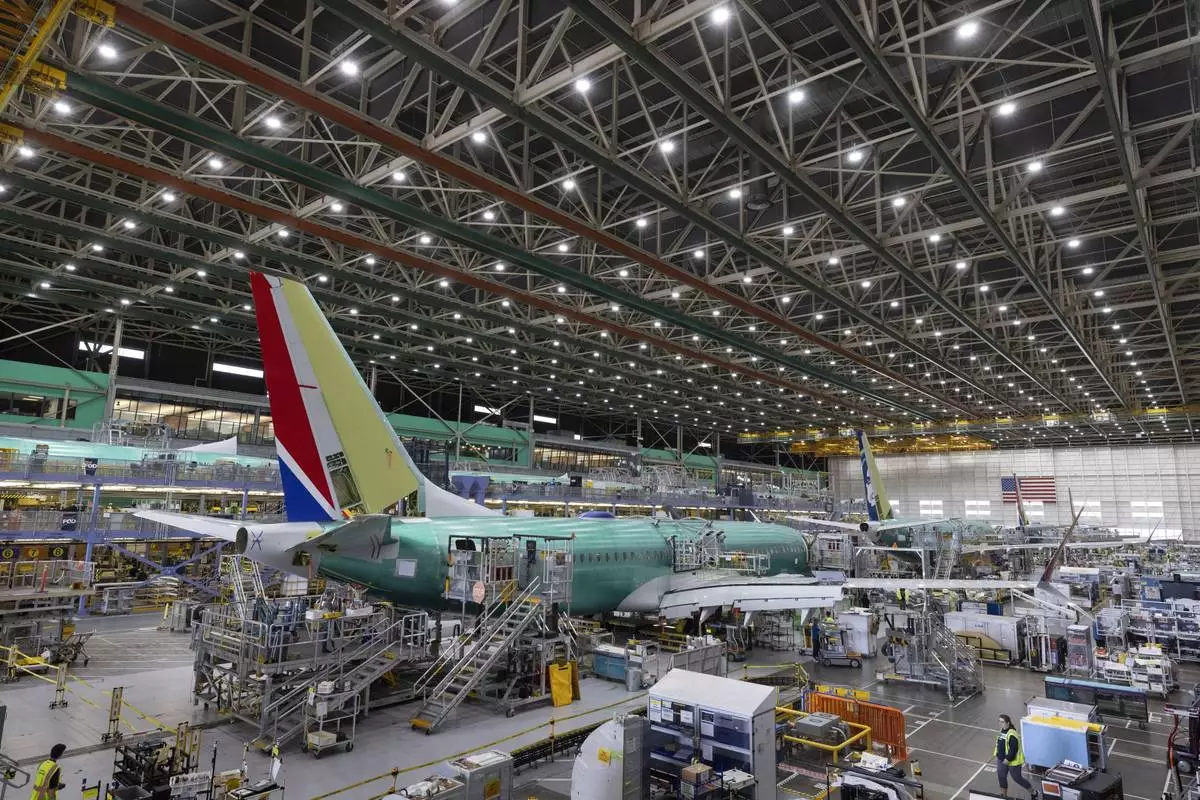

FILE - Boeing employees work on the 737 MAX on the final assembly line at Boeing's Renton plant, June 15, 2022, in Renton, Wash. (Ellen M. Banner/The Seattle Times via AP, Pool, File)
SEOUL. South Korea (AP) — The United States has blocked imports of sea salt products from a major South Korean salt farm accused of using slave labor, becoming the first trade partner to take punitive action against a decadeslong problem on salt farms in remote islands off South Korea’s southwest coast.
U.S. Customs and Border Protection issued a withhold release order against the Taepyung salt farm, saying information “reasonably indicates” the use of forced labor at the company in the island county of Sinan, where most of South Korea’s sea salt products are made.
Under the order issued last Wednesday, Customs personnel at all U.S. ports of entry are required to hold sea salt products sourced from the farm.
Taepyung is the largest salt farm in Sinan, reportedly producing about 16,000 tons of salt annually, which accounts for approximately 6% of the country’s total output, and is a major supplier to South Korean food companies. The farm, located on Jeungdo island in Sinan and leasing most of its salt fields to tenants, has been repeatedly accused of using forced labor, including in 2014 and 2021.
In a statement to The Associated Press on Monday, South Korea’s Foreign Ministry said relevant government agencies, including the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, have been taking steps to address labor practices at Taepyung since 2021, and it assesses that none of the salt produced there now is sourced from forced labor. The ministry said it plans to “actively engage” in discussions with the U.S. officials over the matter. The fisheries ministry didn’t immediately comment on the U.S. move.
The widespread slavery at Sinan’s salt farms was exposed in 2014, when dozens of slavery victims — most of them with disabilities — were rescued from the islands following an investigation by mainland police. Some of their stories were documented by The Associated Press, which highlighted how slavery persisted despite the exposure.
U.S. Customs said it identified several signs of forced labor during its investigation of Taepyung, including “abuse of vulnerability, deception, restriction of movement, retention of identity documents, abusive living and working conditions, intimidation and threats, physical violence, debt bondage, withholding of wages, and excessive overtime.”
Lawyer Choi Jung Kyu, part of a group of attorneys and activists who petitioned U.S. Customs to take action against Taepyung and other South Korean salt farms in 2022, expressed hope that the U.S. ban would increase pressure on South Korea to take more effective steps to eliminate the slavery.
“Since the exposure of the problem in 2014, the courts have recognized the legal responsibility of the national government and local governments, but forced labor among salt farm workers has not been eradicated,” Choi said. “Our hope is that the export ban would force companies to strengthen due diligence over supply chains and lead to the elimination of human rights violations.”
Most of the salt farm slaves rescued in 2014 had been lured to the islands to work by brokers hired by salt farm owners, who would beat them into long hours of hard labor and confine them at their houses for years while providing little or no pay.
The slavery was revealed in early 2014 when two police officers from the capital, Seoul, disguised themselves as tourists to clandestinely rescue a victim who had been reported by his family as missing. One of the Seoul police officers told AP they went undercover because of concerns about collaboration between the island’s police and salt farm owners. Dozens of farm owners and job brokers were indicted, but no police or officials were punished despite allegations some knew about the slavery.
In 2019, South Korea’s Supreme Court upheld a lower court ruling that ordered the government to compensate three men who had been enslaved on Sinan’s salt farms, acknowledging that local officials and police failed to properly monitor their living and working conditions.
The salt farm slavery issue resurfaced in 2021 when around a dozen workers at Taepyung were discovered to have endured various labor abuses, including forced labor and wage theft.
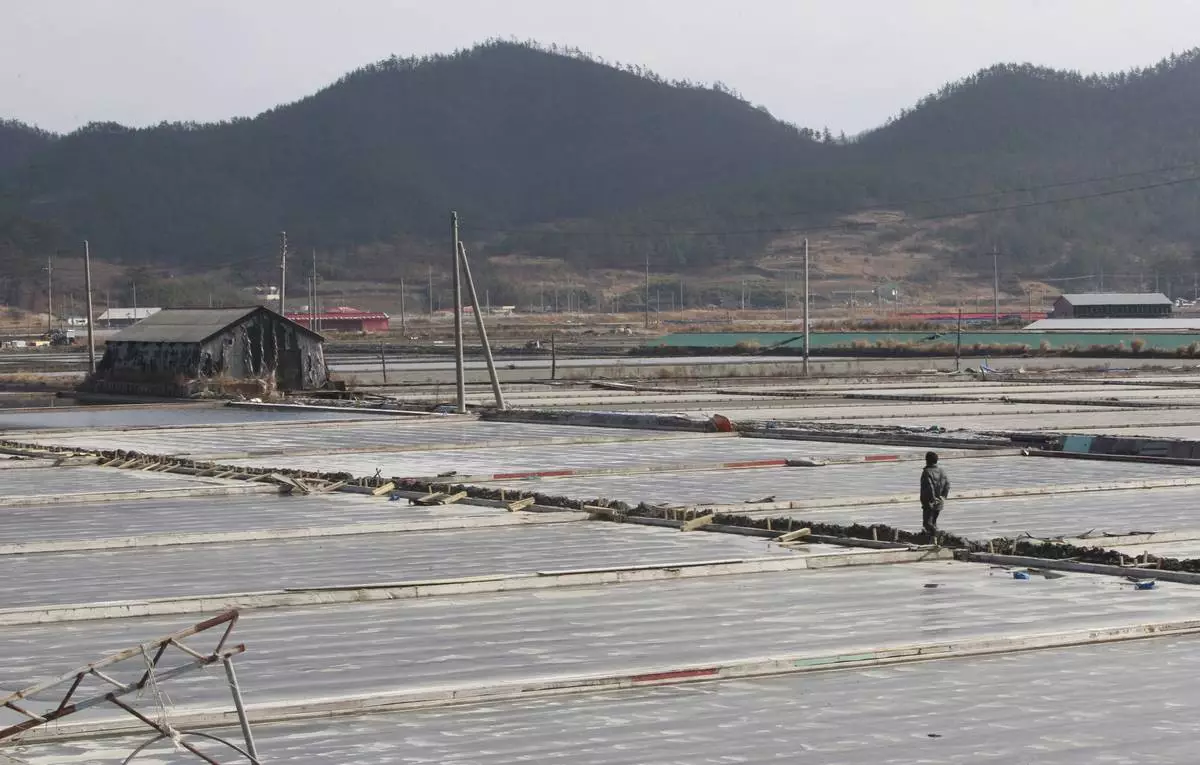

FILE - A salt farm owner walks around his salt farm on Sinui Island, South Korea, Feb. 19, 2014. (AP Photo/Ahn Young-joon, File)