Ukraine fired six U.S.-made ATACMS missiles at Russia’s Bryansk region, Russia’s Defense Ministry said Tuesday, days after U.S. President Joe Biden eased restrictions on Ukrainian use of American-made weapons in the war that has reached its 1,000-day milestone.
Ukraine claimed it hit a military weapons depot in Bryansk in the middle of the night, though it didn't specify what weapons it used. The Ukrainian General Staff said that multiple explosions and detonation were heard in the targeted area.
Click to Gallery
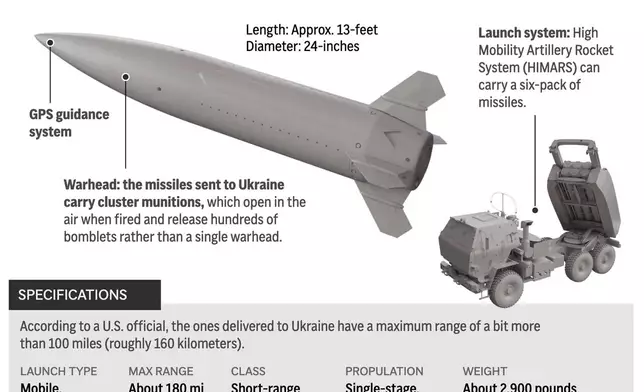
The graphic above shows the long-range U.S. ATACMS missile system components. The U.S. will allow Ukraine to use American-supplied longer-range weapons to conduct strikes inside Russian territory. (AP Digital Embed)
In this photo provided by the Ukrainian Emergency Services on Nov. 19, 2024, rescue workers clear the rubble of a residential building destroyed by a Russian strike in Hlukhiv, Ukraine. (Ukrainian Emergency Service via AP)
In this photo provided by the Ukrainian Emergency Services on Nov. 19, 2024, rescue workers clear the rubble of a residential building destroyed by a Russian strike in Hlukhiv, Ukraine. (Ukrainian Emergency Service via AP)
In this photo provided by the Ukrainian Emergency Services on Nov. 19, 2024, rescue workers clear the rubble of a residential building destroyed by a Russian strike in Hlukhiv, Ukraine. (Ukrainian Emergency Service via AP)
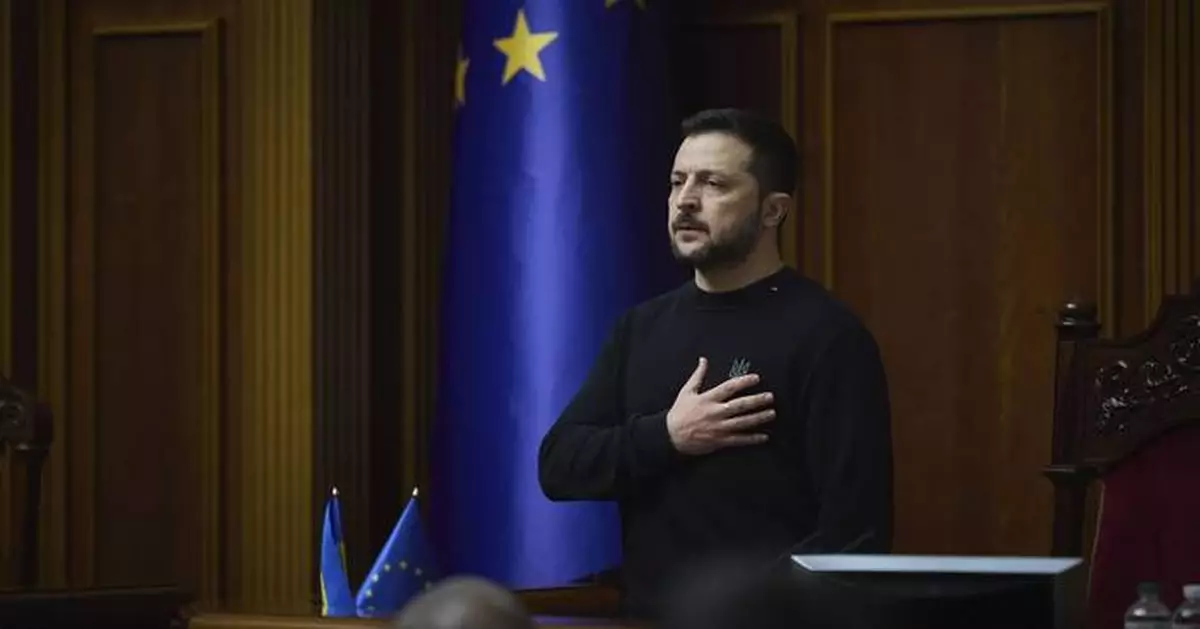
In this photo provided by the Press Service Of The President Of Ukraine on Nov. 19, 2024, Ukraine's President Volodymyr Zelenskyy speaks to parliamentarians at Verkhovna Rada in Kyiv, Ukraine. (Press Service Of The President Of Ukraine via AP)
In this photo provided by the Press Service Of The President Of Ukraine on Nov. 19, 2024, Ukraine's President Volodymyr Zelenskyy listens to the national anthem before his speech at Verkhovna Rada in Kyiv, Ukraine. (Press Service Of The President Of Ukraine via AP)
In a statement carried by Russian news agencies, the Russian Defense Ministry said the military shot down five Army Tactical Missile System, known as ATACMS, and damaged one more.
The fragments fell on the territory of an unspecified military facility, the ministry said. The falling debris sparked a fire, but didn’t inflict any damage or casualties, it said.
Neither side's claims could be independently verified.
The announcement came after Biden authorized Ukraine to use U.S.-supplied missiles to strike deeper inside Russia, easing limitations on the longer range weapons after Russia deployed thousands of North Korean troops in the conflict.
Earlier on Tuesday, Ukrainian officials reported a third Russian strike in three days on a civilian residential area in Ukraine killed at least 12 people, including a child.
The strike by a Shahed drone in the northern Sumy region late Monday hit a dormitory of an educational facility in the town of Hlukhiv and wounded 11 others, including two children, authorities said, adding that more people could be trapped under the rubble.
Ukrainian civilians have repeatedly been clobbered by Russian drones and missiles during the war, while on the battlefield it is under severe Russian pressure at places on the about 1,000-kilometer (600-mile) front line where its army is stretched thin against a bigger adversary.
On Sunday, a Russian ballistic missile with cluster munitions struck a residential area of Sumy in northern Ukraine, killing 11 people and wounding 84 others. On Monday, a Russian missile barrage sparked apartment fires in the southern port of Odesa, killing at least 10 people and wounding 43.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said that the series of aerial strikes proved that Russian President Vladimir Putin wasn't interested in ending the war.
“Each new attack by Russia only confirms Putin’s true intentions. He wants the war to continue. Talks about peace are not interesting to him. We must force Russia to a just peace by force,” Zelenskyy said.
Follow AP’s coverage of the war in Ukraine at https://apnews.com/hub/russia-ukraine
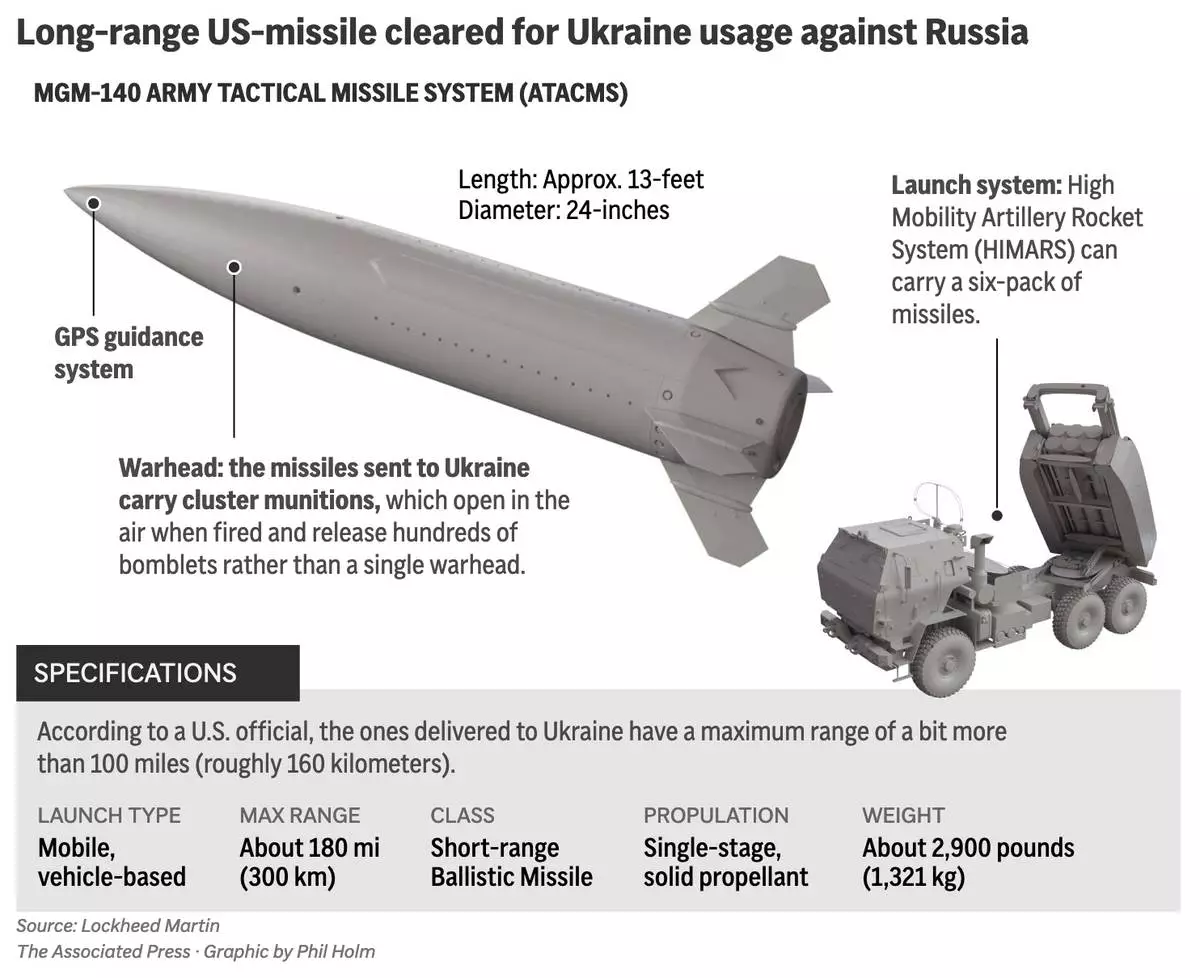
The graphic above shows the long-range U.S. ATACMS missile system components. The U.S. will allow Ukraine to use American-supplied longer-range weapons to conduct strikes inside Russian territory. (AP Digital Embed)
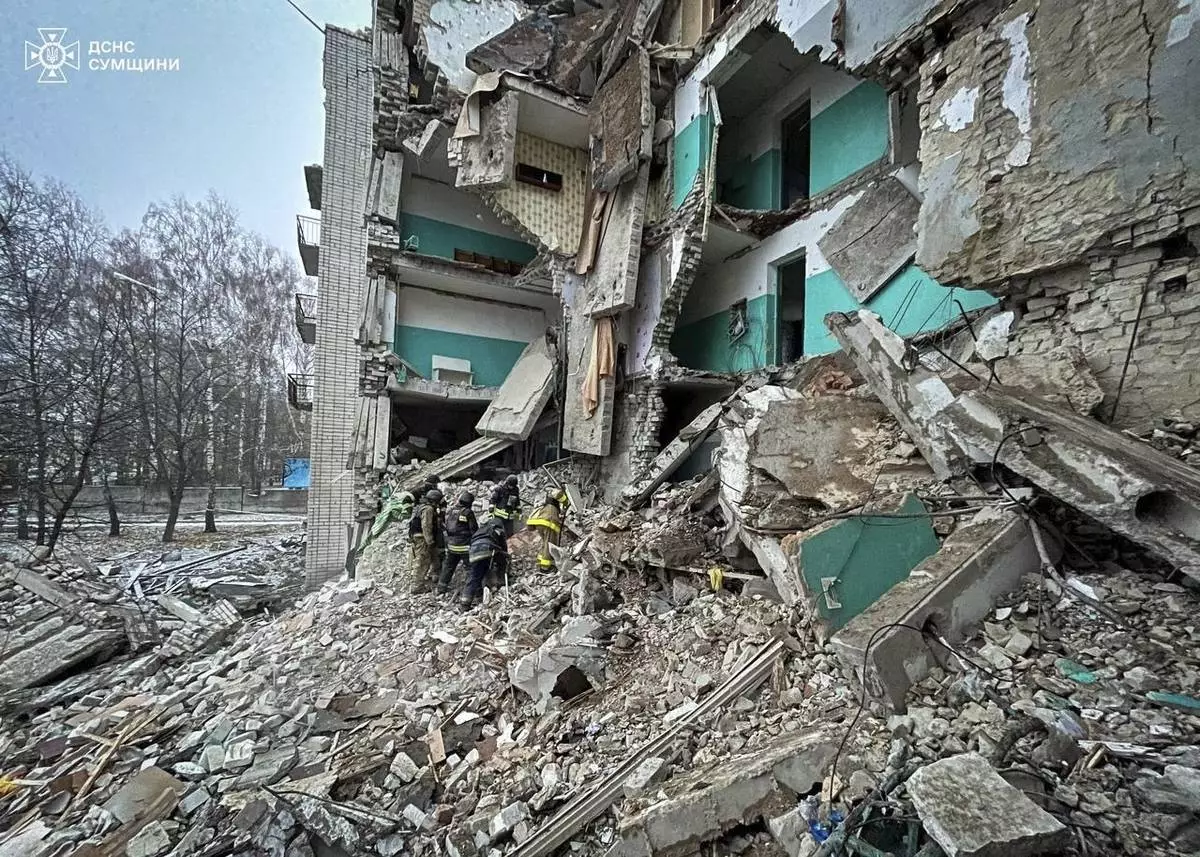

In this photo provided by the Ukrainian Emergency Services on Nov. 19, 2024, rescue workers clear the rubble of a residential building destroyed by a Russian strike in Hlukhiv, Ukraine. (Ukrainian Emergency Service via AP)
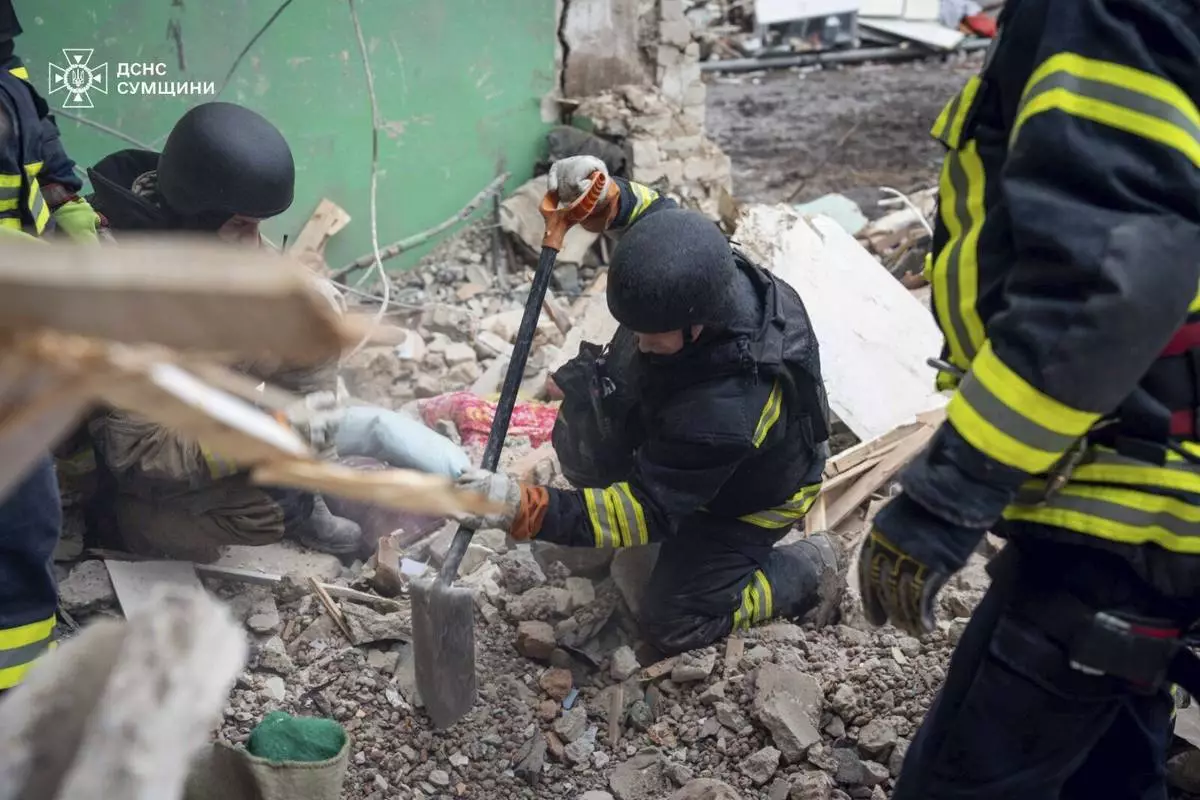

In this photo provided by the Ukrainian Emergency Services on Nov. 19, 2024, rescue workers clear the rubble of a residential building destroyed by a Russian strike in Hlukhiv, Ukraine. (Ukrainian Emergency Service via AP)
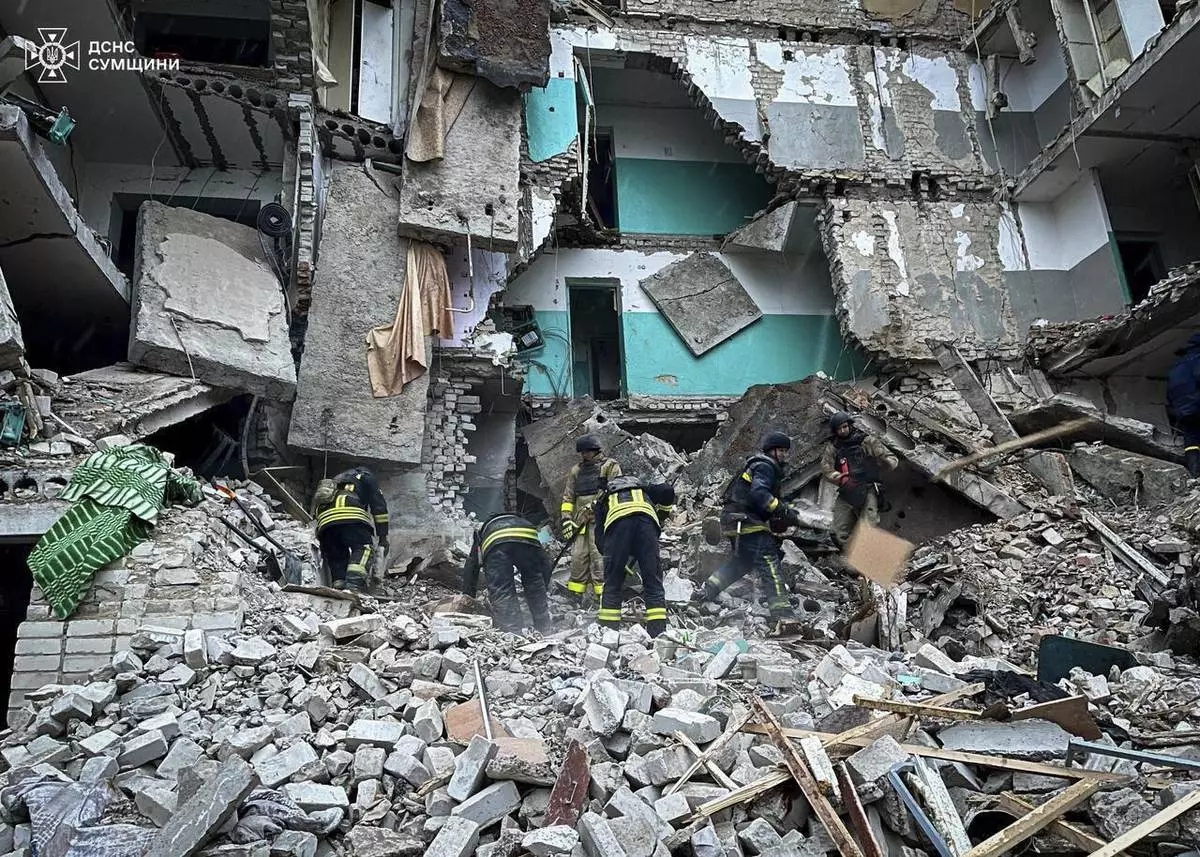

In this photo provided by the Ukrainian Emergency Services on Nov. 19, 2024, rescue workers clear the rubble of a residential building destroyed by a Russian strike in Hlukhiv, Ukraine. (Ukrainian Emergency Service via AP)
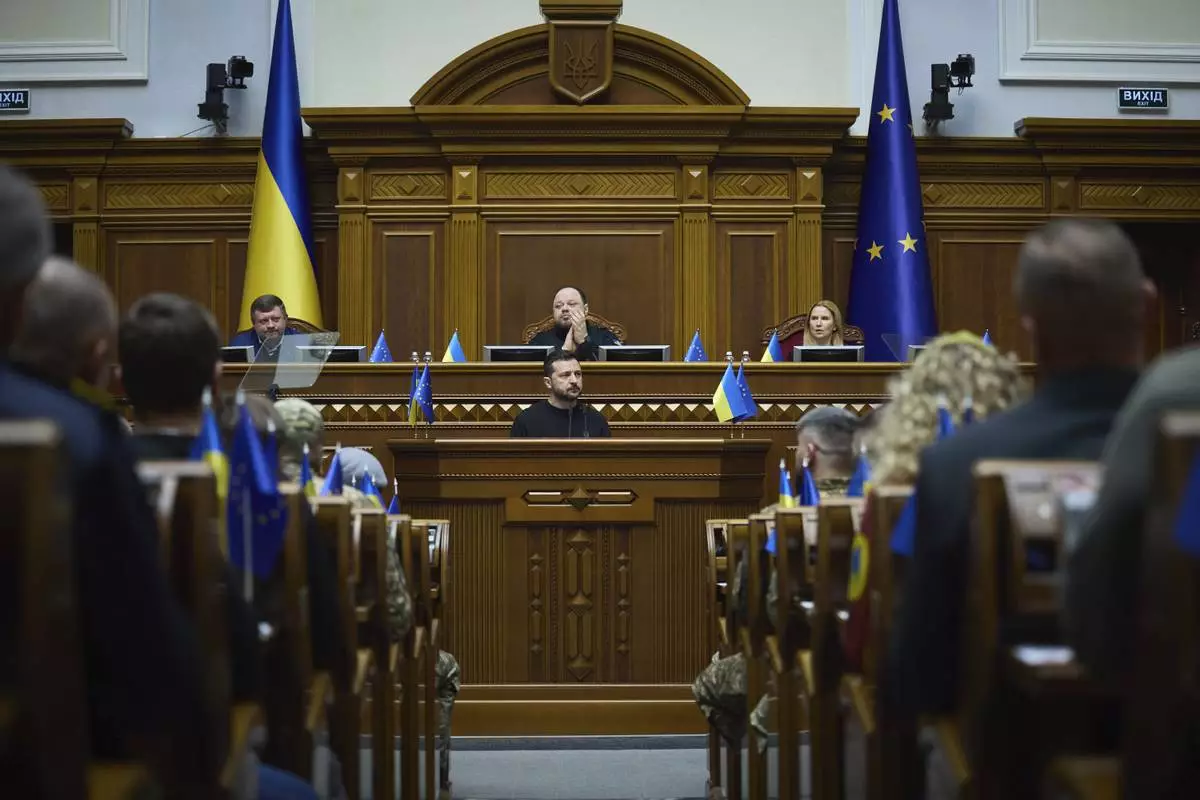

In this photo provided by the Press Service Of The President Of Ukraine on Nov. 19, 2024, Ukraine's President Volodymyr Zelenskyy speaks to parliamentarians at Verkhovna Rada in Kyiv, Ukraine. (Press Service Of The President Of Ukraine via AP)
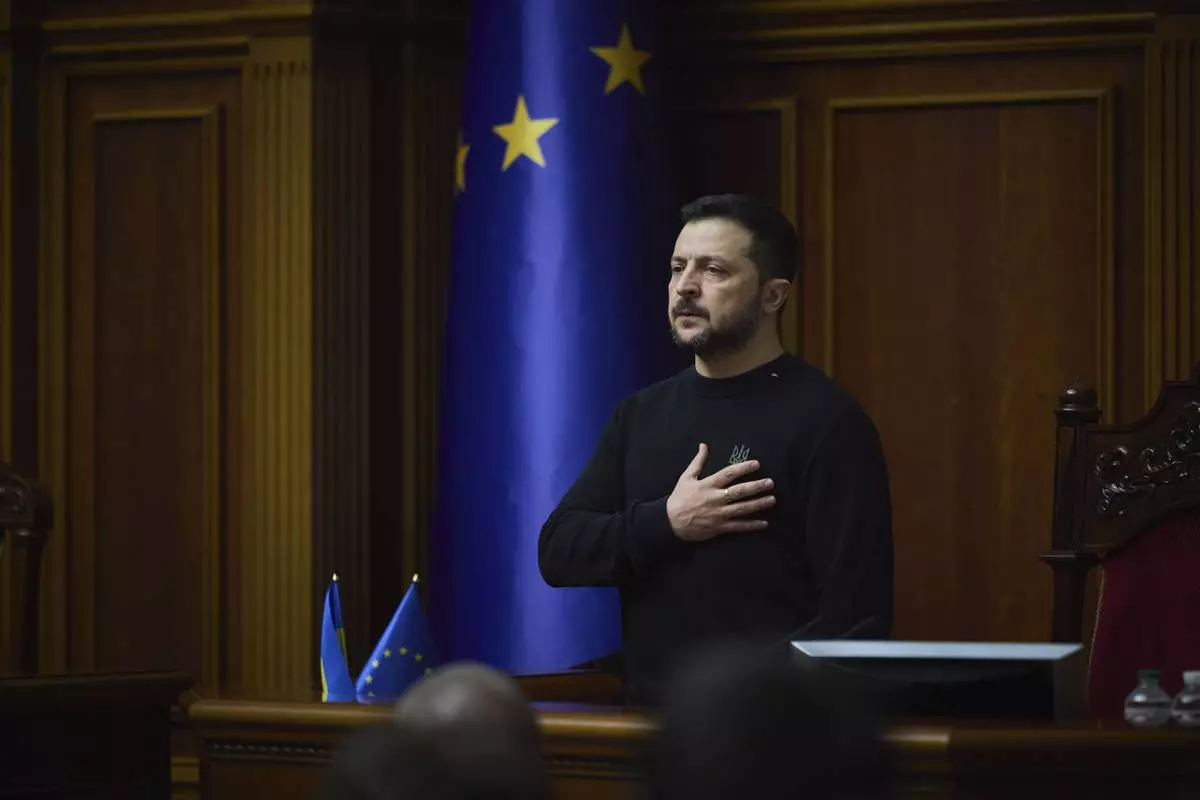

In this photo provided by the Press Service Of The President Of Ukraine on Nov. 19, 2024, Ukraine's President Volodymyr Zelenskyy listens to the national anthem before his speech at Verkhovna Rada in Kyiv, Ukraine. (Press Service Of The President Of Ukraine via AP)
BAKU, Azerbaijan (AP) — Just as a simple lever can move heavy objects, rich nations are hoping another kind of leverage — the financial sort — can help them come up with the money that poorer nations need to cope with climate change.
It involves a complex package of grants, loans and private investment, and it's becoming the major currency at annual United Nations climate talks known as COP29.
But poorer nations worry they’ll get the short end of the lever: not much money and plenty of debt.
Meanwhile, half a world away in Brazil, leaders of the 20 most powerful economies issued a statement that among other things gave support to strong financial aid for climate for poor nations and the use of leverage financial mechanisms. That was cheered by climate analysts and advocates.
Money is the key issue in Baku, where negotiators are working on a new amount of cash for developing nations to transition to clean energy, adapt to climate change and deal with weather disasters. It’ll replace the current goal of $100 billion annually — a goal set in 2009.
Negotiators are fighting over three big parts of the issue: How big the numbers are, how much is grants or loans, and who pays. The how big question is the toughest to negotiate and will likely be resolved only after the first two are solved, COP29 lead negotiator Yalchin Rafiyev told The Associated Press in an interview Tuesday.
“There are interlinkages of the elements. That’s why having one of them agreed could unlock the other one,” Rafiyev said.
It's like the first domino falling leading to another, he said.
In these negotiations, rich potential donor nations have been reluctant to offer a starting figure to negotiate from. So Rafiyev said the conference presidency is putting the pressure on them, telling “the developed countries that the figure should be fair and ambitious, corresponding to the needs and priorities of the world.”
Experts put the need closer to $1 trillion, while developing nations have said they'll need $1.3 trillion in climate finance. But negotiators are talking about different types of money as well as amounts.
So far rich nations have not quite offered a number for the core of money they could provide. But the European Union is expected to finally do that and it will likely be in the $200 to $300 billion a year range, Linda Kalcher, executive director of the think tank Strategic Perspectives, said Tuesday. It might be even as much as four times the original $100 billion, said Luca Bergamaschi, co-founding director of the Italian ECCO think tank.
But there's a big difference between $200 billion and $1.3 trillion. That can be bridged with “the power of leverage," said Avinash Persaud, climate adviser for the Inter-American Development Bank.
When a country gives a multilateral development bank like his $1, it could be used with loans and private investment to get as much as $16 in spending for transitioning away from dirty energy, Persaud said. When it comes to spending to adapt to climate change, the bang for the buck, is a bit less, about $6 for every dollar, he said.
But when it comes to compensating poor nations already damaged by climate change — such as Caribbean nations devastated by repeated hurricanes — leverage doesn't work because there's no investment and loans. That's where straight-out grants could help, Persaud said.
Whatever the form of the finance, Ireland’s environment minister Eamon Ryan said it would be “unforgivable” for developed countries to walk away from negotiations in without making a firm commitment toward developing ones.
“We have to make an agreement here,” he said. "We do have to provide the finance, particularly for the developing countries, and to give confidence that they will not be excluded, that they will be center stage.”
If climate finance comes mostly in the form of loans, it means more debt for nations that are already drowning in it, said Michai Robertson, climate finance negotiator for the Alliance of Small Island States.
“All of these things are just nice ways of saying more debt,” Robertson said.
His organization argues that most of the $1.3 trillion it seeks should be in grants and very low-interest and long-term loans that are easier to pay back. Only about $400 billion should be in leveraged loans, Robertson said.
Leverage from loans “will be a critical part of the solution,” said United Nations Environment Programme Director Inger Andersen. But so must grants and so must debt relief, she added.
Rohey John, Gambia's environment minister, said the absence of a financial commitment from rich nations suggests “they are not interested in the development of the rest of the mankind.”
“Each and every day we wake up to a crisis that will wipe out a whole community or even a whole country, to a crime that we never committed," she said.
Ministers giving their national statements also came out with fighting words.
“Our children, our elderly, our women, our girls, our Indigenous people, our youth deserve better,” said St. Kitts and Nevis Climate Minister Joyelle Clarke. “Let us be seized by a desire for better."
Cuban environment minister Armando Rodriguez Batista urged countries not to “favor death over life.”
The G20's mention of the need for strong climate finance and especially the replenishment of the International Development Association gives a boost to negotiators in Baku, ECCO's Bergamaschi said.
“G20 Leaders have sent a clear message to their negotiators at COP29: do not leave Baku without a successful new finance goal,” United Nations climate secretary Simon Stiell said. “This is an essential signal, in a world plagued by debt crises and spiraling climate impacts, wrecking lives, slamming supply chains and fanning inflation in every economy.”
Analysts and activists said they were also worried because the G20 statement did not repeat the call for a transition away from fossil fuels, a hard-fought concession at last year's climate talks.
Veteran climate talks analyst Alden Meyer of the European think tank E3G said the watering down of the G20 statement on fossil fuel transition is because of pressure by Russia and Saudi Arabia. He said it is "just the latest reflection of the Saudi wrecking ball strategy" at climate meetings.
The Associated Press’ climate and environmental coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.

People listen to speeches during a plenary session at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
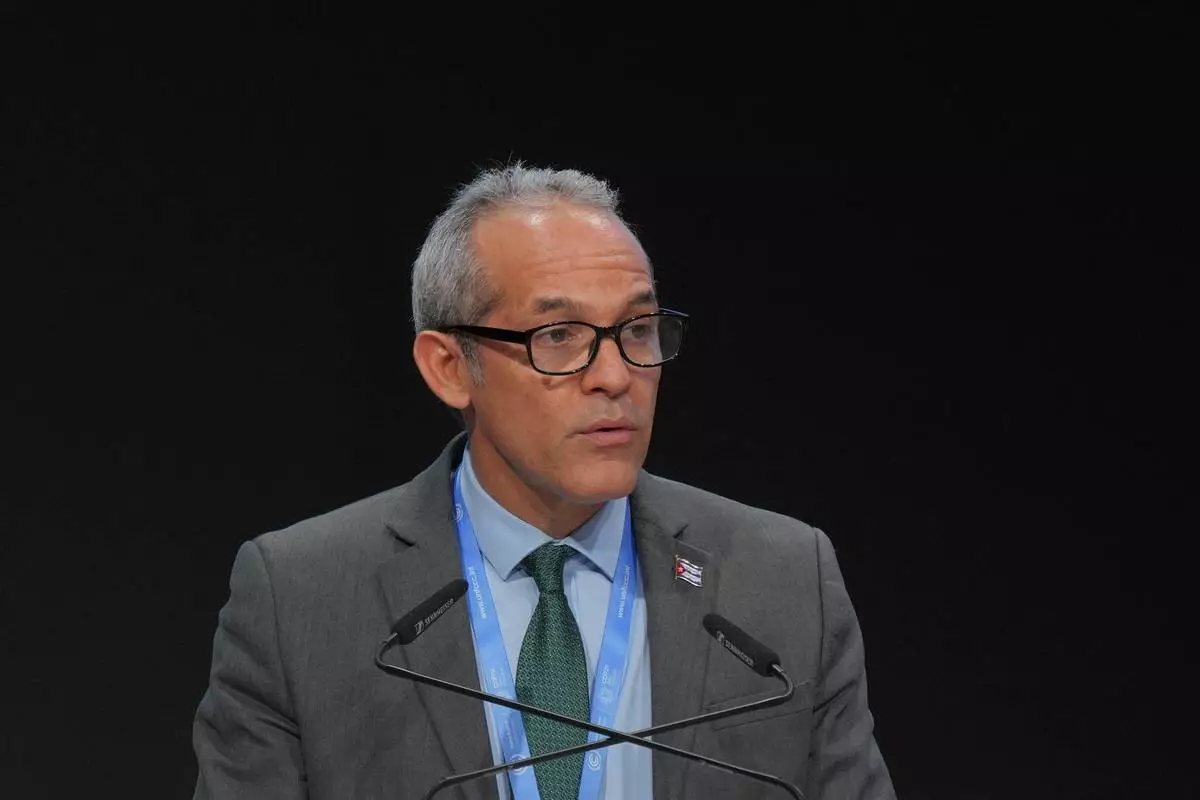

Cuba Environment Minister Armando Rodriguez Batista speaks during a plenary session at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
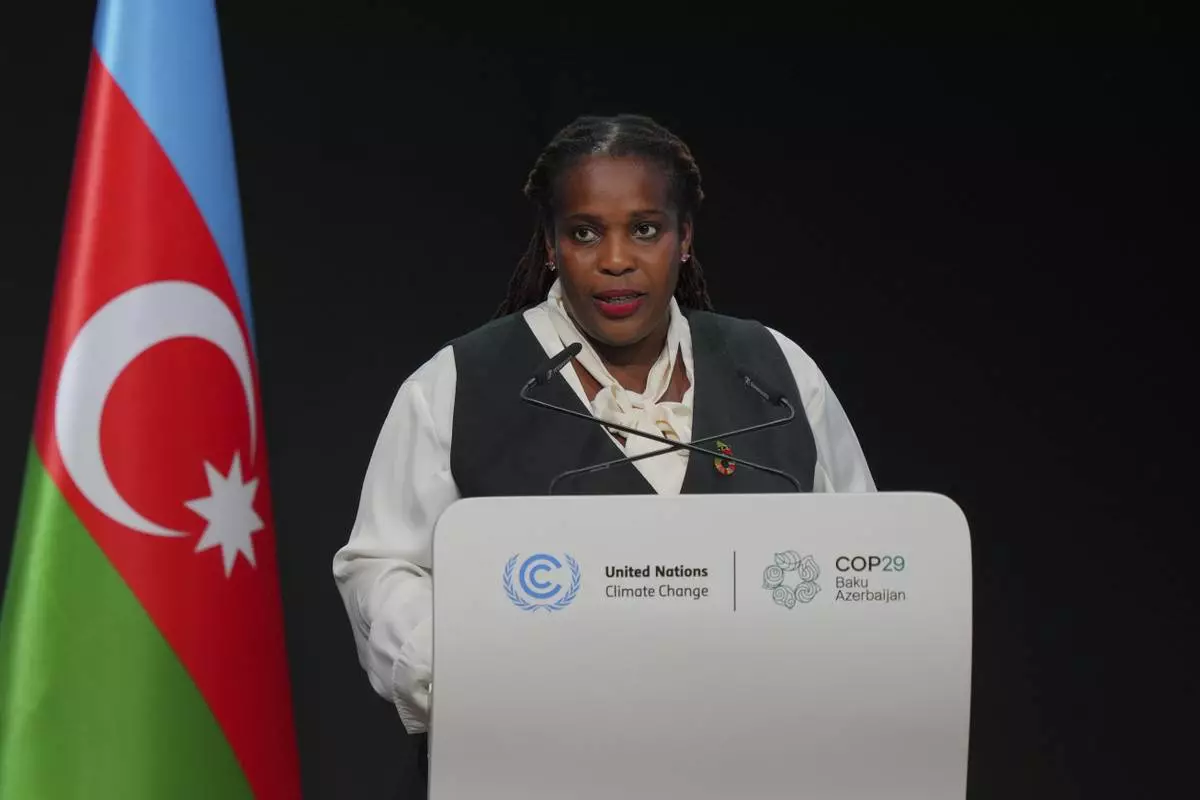

St. Kitts and Nevis Climate Minister Joyelle Clarke speaks during a plenary session at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)
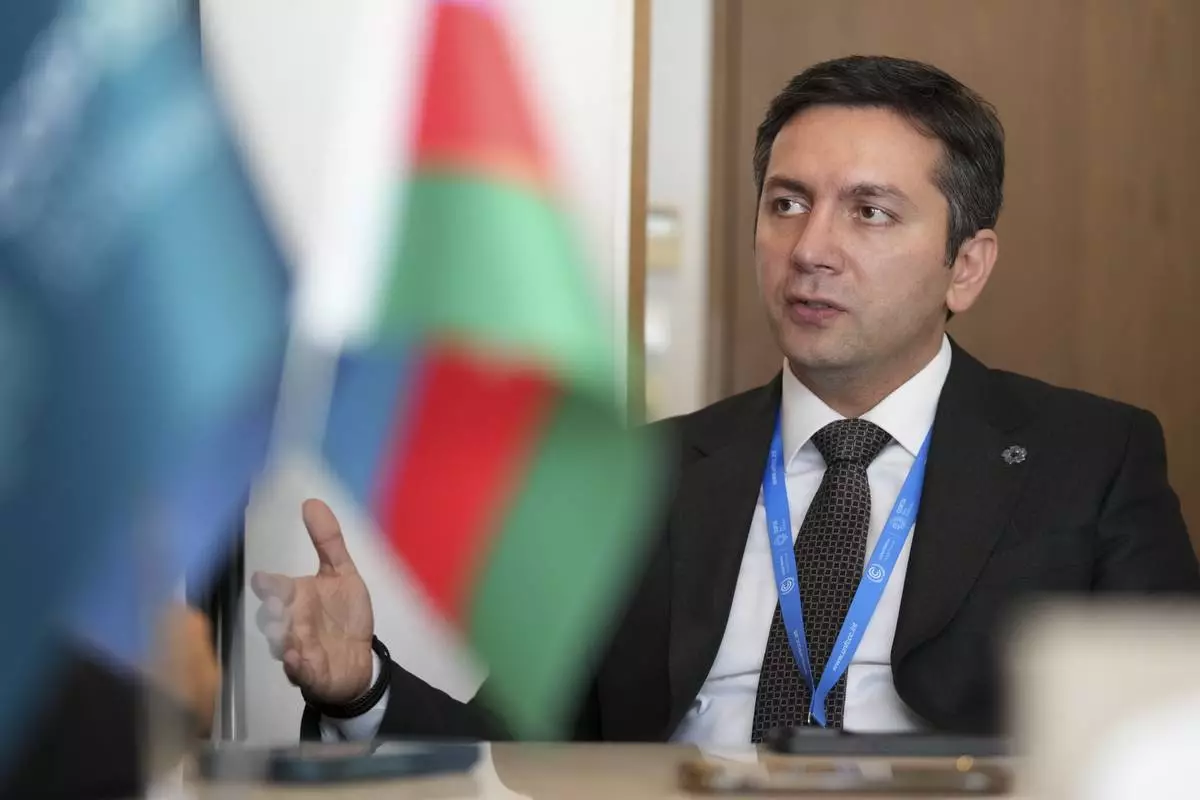

Yalchin Rafiyev, Azerbaijan's COP29 lead negotiator, speaks during an interview with The Associated Press at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)
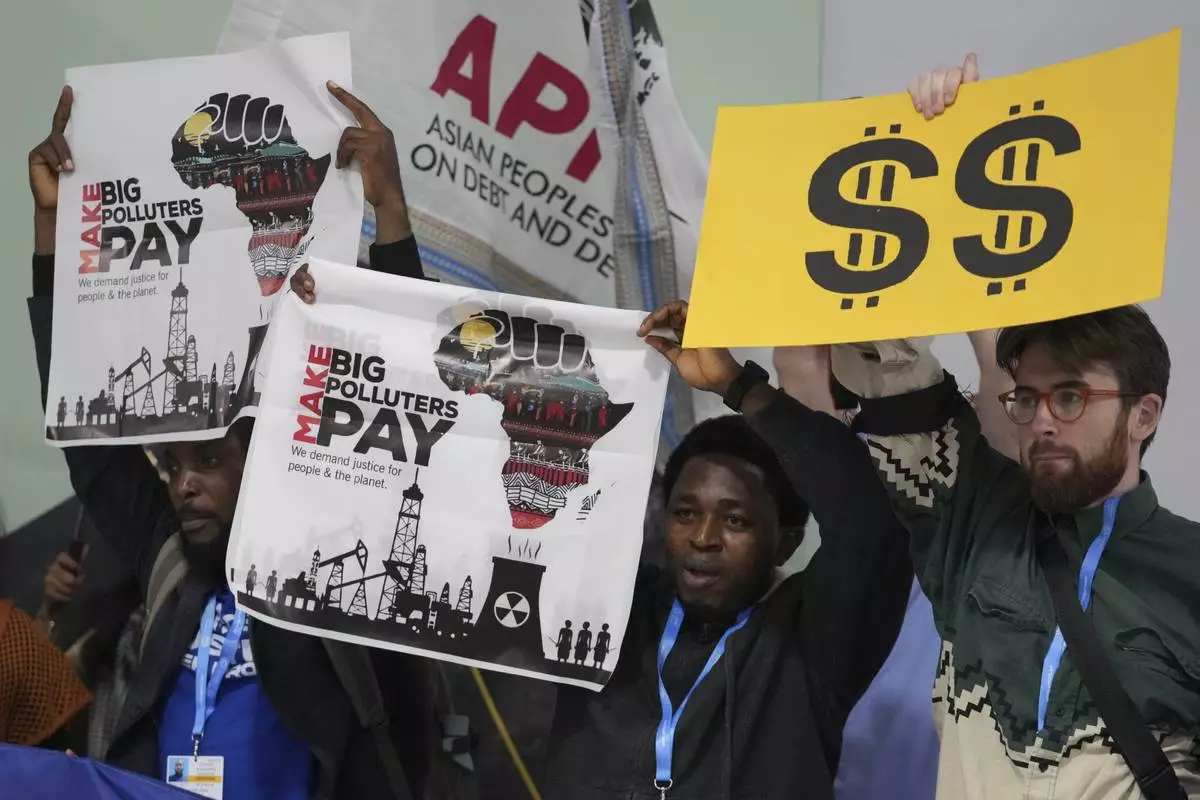

Activists participate in a demonstration for climate finance at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)
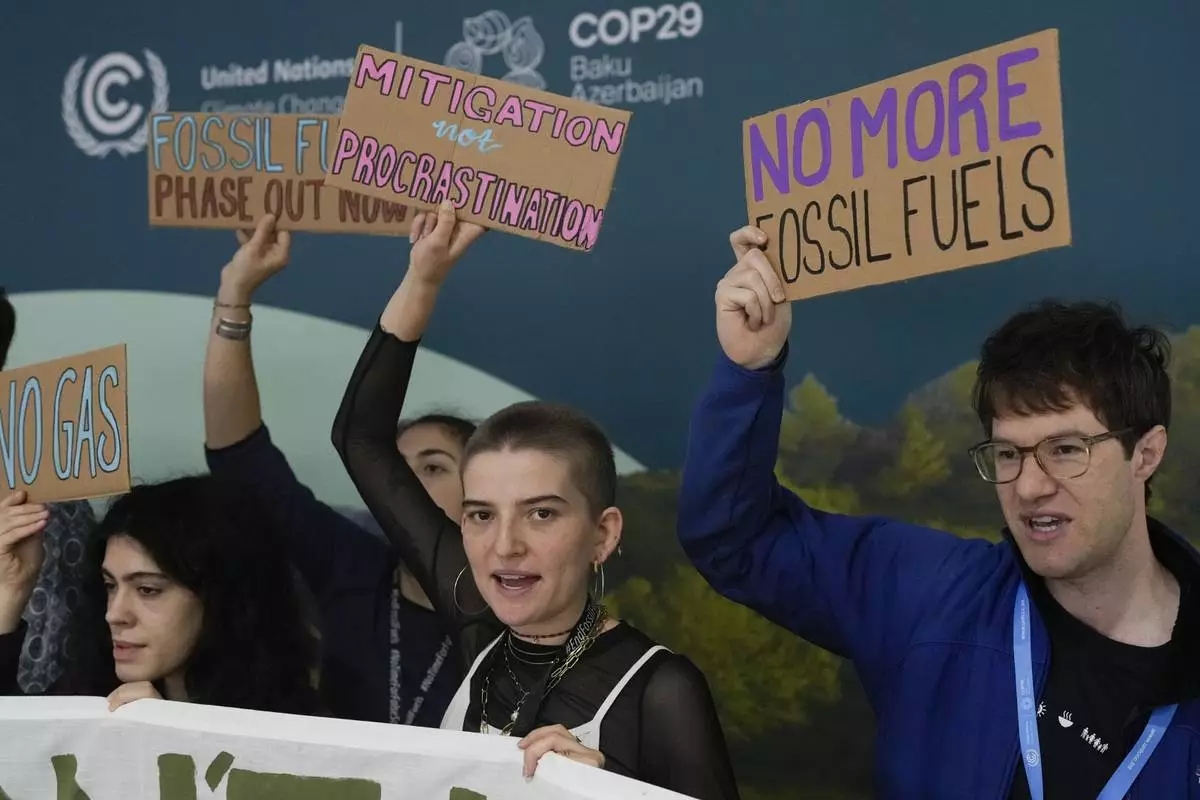

Activists participate in a demonstration against fossil fuels at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)

People arrive for the day at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Joshua A. Bickel)

Bolivia foreign policy director and Like-Minded Group chair Diego Balanza speaks during a plenary session at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)

Activists participate in a demonstration for climate finance at the COP29 U.N. Climate Summit, Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024, in Baku, Azerbaijan. (AP Photo/Peter Dejong)